Efficiency and precision in supply chain operations are now more important than ever in today’s tech-driven, fast-paced environment. The smart warehouse is a revolutionary development in logistics that uses advanced technology to improve overall production, speed up procedures, and lower errors. However, what is a smart warehouse, and why is it crucial to modern intralogistics? Let us investigate.
What Is a Smart Warehouse?
To build a completely connected and optimised operating ecosystem, a smart warehouse combines cutting-edge technology like automation, artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and data analytics. Technologies, like IoT and automation, can help solve supply chain issues and integrate smart environments. Smart warehouses, as opposed to traditional warehouses, guarantee smooth coordination between several operations, from inventory management to order fulfilment, automate repetitive jobs, and offer real-time analytics.
Core Technologies in Smart Warehousing
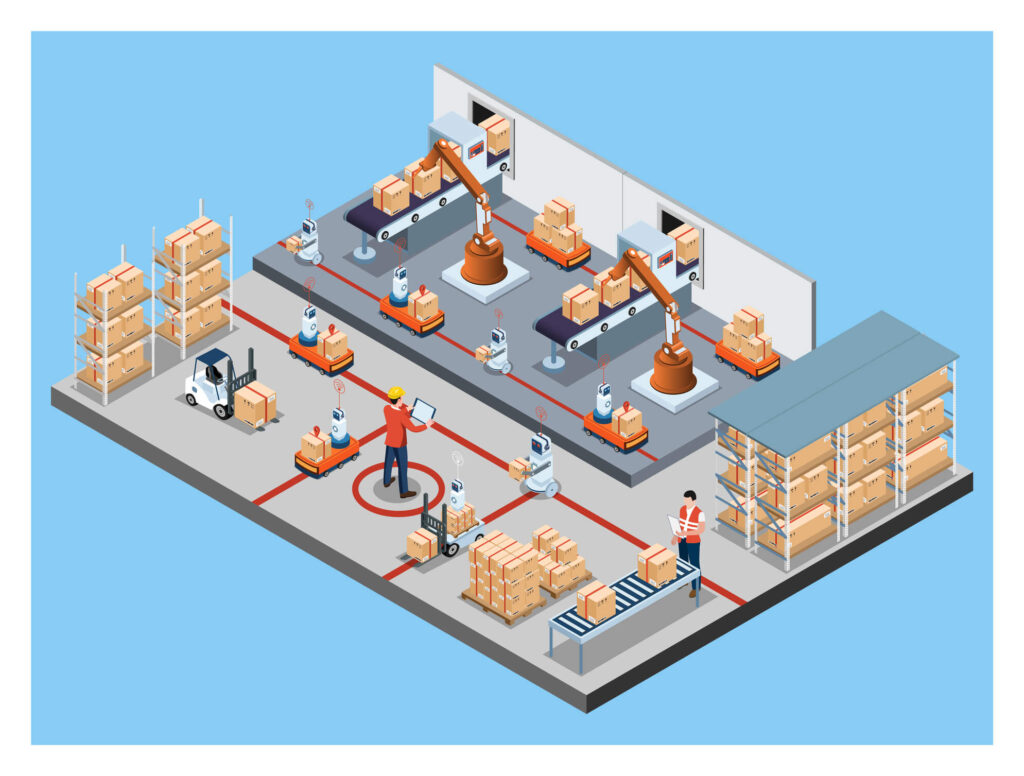
- Internet of Things (IoT) – IoT-enabled devices and sensors play a vital role in monitoring inventory levels, tracking shipments, and ensuring ideal storage conditions. For instance, sensors can detect temperature fluctuations for perishable goods, triggering automated alerts to maintain compliance.
- Automation and robotics – robotics such as Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) and Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) are revolutionising material handling. They streamline tasks like picking, packing, and transporting goods, reducing manual labor and increasing accuracy. Alongside human workers, large language models (LLM)-enabled robots can ensure jobs are executed accurately and effectively by understanding complex verbal instructions, offering real-time support, or asking clarifying questions.
- Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) – WMS platforms are the brains of a smart warehouse, integrating with other technologies to provide real-time inventory visibility, workflow management, and advanced analytics.
- Artificial intelligence and machine learning – AI-driven algorithms forecast demand, predict inventory needs, and optimise routing for deliveries. Machine learning further refines these predictions over time, helping businesses reduce waste and improve efficiency.
- Augmented Reality (AR) – AR technology enhances worker productivity by overlaying digital instructions onto the physical environment. Wearable AR devices assist with navigation, picking, and assembly tasks.
Blockchain for supply chain transparency – Blockchain technology ensures secure, immutable records of transactions, enhancing traceability and trust within the supply chain. If further implemented in warehouse automation, blockchain technology could increase supply chain transparency, from 8% in 2019 to even 45% by 2030.
Key Benefits of Smart Warehousing
Real-Time Visibility
IoT sensors and connected systems offer end-to-end visibility into inventory and operations. This enables businesses to track shipments, monitor stock levels, and respond swiftly to disruptions.
Enhanced Operational Efficiency
Automation and robotics reduce manual errors, speed up repetitive tasks, and optimise space utilisation. For example, automated storage and retrieval systems significantly enhance throughput rates.
Improved Accuracy
Smart technologies minimise human errors in processes like inventory counts and order picking, ensuring customers receive the correct products on time.
Scalability
Smart warehousing systems are designed to grow alongside business needs. As demand fluctuates, automated systems can adapt to handle higher volumes without requiring major infrastructure changes.
Sustainability
Energy-efficient technologies and data-driven optimisation reduce waste and emissions, contributing to greener supply chain practices.
Real-World Applications
Smart warehouses are transforming various industries:
E-commerce
Robotics and artificial intelligence are key components used by businesses like Amazon to handle large order volumes and expedite product delivery. Delivery on the same day or the following day is made possible by automated picking systems that use AI algorithms to find and collect products at an unmatched speed. Businesses may also anticipate demand trends with AI-driven forecasting tools, which guarantees they have the proper products on hand when they’re needed.
Retail
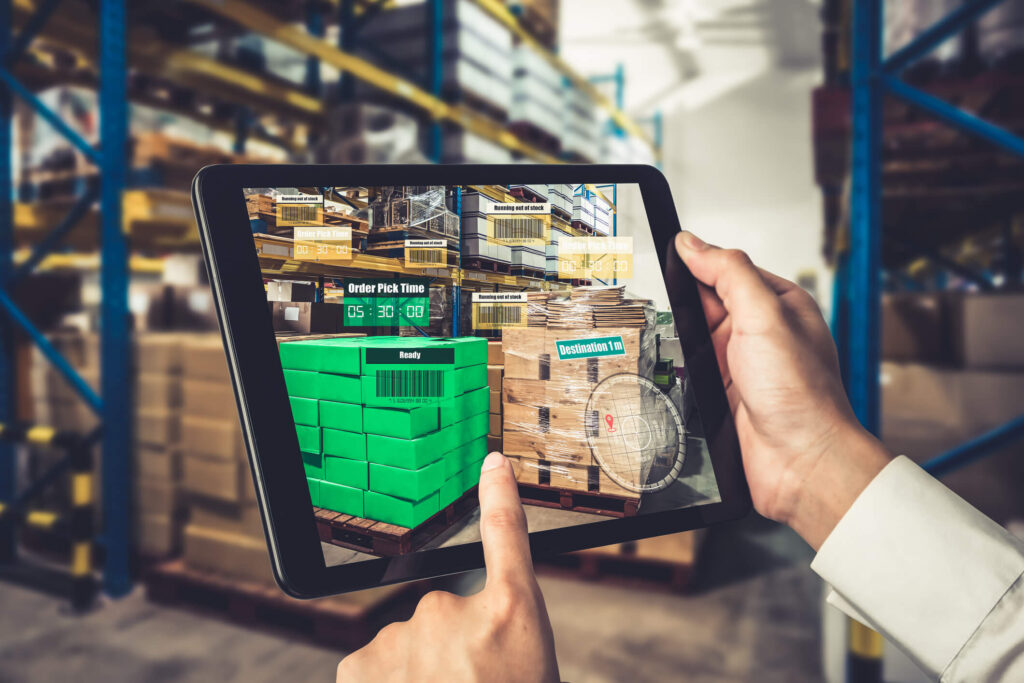

Smart technologies are used by retailers to improve the shopping experience by ensuring appropriate stock levels and expediting delivery times. IoT-enabled inventory solutions, for instance, monitor product availability in real time, guaranteeing that shelves are consistently filled with client favourites. Restocking and picking tasks are streamlined by autonomous robots or robotic arms, which also shorten the time between placing an order and its delivery.
Pharmaceuticals
IoT sensors monitor storage conditions to make sure that stringent regulatory requirements are met. Sensors for temperature and humidity are very important for preserving the integrity of vaccines and delicate drugs. By producing an unchangeable record of handling and storage conditions, blockchain technologies further increase transparency and provide authorities and pharmaceutical businesses with assurances on the quality and safety of their medicines.
Challenges to Implementation
While the benefits of smart warehouses are undeniable, there are challenges to consider:
- Implementing advanced technologies requires significant upfront investment.
- Employees must be trained to work alongside advanced systems, necessitating new skill sets.
- With increased connectivity comes the risk of cyberattacks, making robust cybersecurity measures essential.
The Future of Smart Warehousing
As technology continues to evolve, the capabilities of smart warehouses will only expand. Innovations like 5G connectivity, advanced robotics, and blockchain for secure data management are poised to redefine the logistics landscape. Businesses that embrace these advancements will be better positioned to meet the challenges of a dynamic and competitive market. Also, human-robot collaboration will only rise, with the shift from industry 4.0 to the fifth industrial revolution, which will impact warehousing and smart factories.
Conclusion
Smart warehouses represent the future of intralogistics, offering unparalleled efficiency, accuracy, and scalability. By leveraging advanced technologies, businesses can not only stay ahead of the curve but also deliver superior value to their customers. As the industry continues to innovate, the smart warehouse will remain at the forefront of supply chain transformation—a true testament to the power of technology in reshaping operations.









