With the development of IoT (Internet of Things) technology, tons of different types of IoT communications have been created and prospered such as Wi-Fi and Bluetooth. Another kind of IoT communication which was brought about by the breakthrough of IoT technology is LoRa. LoRa (short for long range) technology is a wireless communication system that enables small amounts of data to be distributed over a wide area. It is a technology that is very common in IIoT industries, especially in long-distance, low-power application scenarios. The technology is highly sensitive and can be identified even if there is a weak signal, which allows for it to reach a much further distance.
It’s only getting stronger too. According to Statista, LoRa connections are expected to reach 730 million in 2023, compared to 470 million in 2022, outlining its importance to IoT industries for the coming year.
“LoRa devices and networks such as the LoRaWAN® enable smart IoT applications that solve some of the biggest challenges facing our planet: energy management, natural resource reduction, pollution control, infrastructure efficiency, and disaster prevention. Semtech’s LoRa devices have amassed several hundred known use cases for smart cities, homes and buildings, communities, metering, supply chain and logistics, agriculture, and more. With hundreds of millions of devices connected to networks in more than 100 countries and growing, LoRa is creating a smarter planet.”
Semtech

How does LoRa technology work?
LoRa is a wireless modulation technique developed by Semtech, which comes from Chirp Spread Spectrum (CSS) technology. Small pulses known as ‘chirp pulses’ are used to encode information via radio waves. LoRa modulated transmission can be received across a wide range of distances and is resistant to disruptions.
Applications that transfer little amounts of data at low bit rates are perfect for LoRa. Compared to technologies like WiFi, Bluetooth, or ZigBee, data can be sent over a greater distance. Due to these characteristics, LoRa is a good choice for low power sensors and actuators.
The licence-free sub-gigahertz bands, such as 915 MHz, 868 MHz, and 433 MHz, are suitable for LoRa operation. In order to attain faster data rates than sub-gigahertz bands, it can also be operated at 2.4 GHz, although at the expense of range. These frequencies fall inside the worldwide ISM bands, which are used only for industrial, scientific, and medical applications.
From a networking standpoint, LoRa simply develops a physical layer approach to wireless transport, such as a transceiver chip. The inability to control traffic for data gathering and endpoint device management means it lacks the appropriate network protocols. This is where LoRaWAN, also known as long-range WAN, enters the picture.
What is LoRaWAN?
The LoRa Alliance created and maintains LoRaWAN, an open, cloud-based standard that facilitates wireless device communication. In essence, LoRaWAN combines networking with LoRa wireless technology and adds security features like node authentication and data encryption. Its purpose is to wirelessly link portable electronic devices to the internet in local, regional, and international networks.
The LoRaWAN specification is a standard that, most crucially, enables smooth integration between devices made by different manufacturers. The adoption of LoRa technology in the IoT sector has accelerated in part due to this one cause.
In fact, according to the LoRa Alliance, there are currently 181 LoRaWAN network operators spread across all four corners of the globe. In addition to this, ABI Research has concluded that, by 2026, LoRa will account for more than a quarter of LPWA network connections, which would make it the leading non-cellular LPWA technology.
So, how does LoRaWAN work?
The LoRaWAN architecture consists of four main parts:
- End Nodes
- Gateway
- Network Server
- Application Server
End nodes
End nodes are devices which are located at the edge of the network. They often have sensors installed to periodically gather and monitor data. Typically, they take the shape of a low-power microcontroller that can be used in the field for many years without requiring any maintenance and is outfitted with a low-power LoRa transmitter to communicate the data packets to the gateway.
Gateways
The connection between the network and the nodes is made by LoRaWAN Gateways. They use a LoRa concentrator to gather data from the end nodes and send it to the network server across the public or private network infrastructure. Since packet forwarding is their main use, gateways are regarded as packet forwarders.
Network server
The cloud LoRa server receives data from the gateways, consolidates it, and then uploads it to the application server. The Things Network is a prime illustration of a network server (TTN).
Application server
You can use the application server to visually or analytically interpret the data. Additionally, you may incorporate the data points into a platform to take an action, such as turning on rainwater pumps for agricultural settings or opening windows in greenhouses to maintain a specific humidity level. Even notification services can be set up to alert engineers when a possible problem might arise.
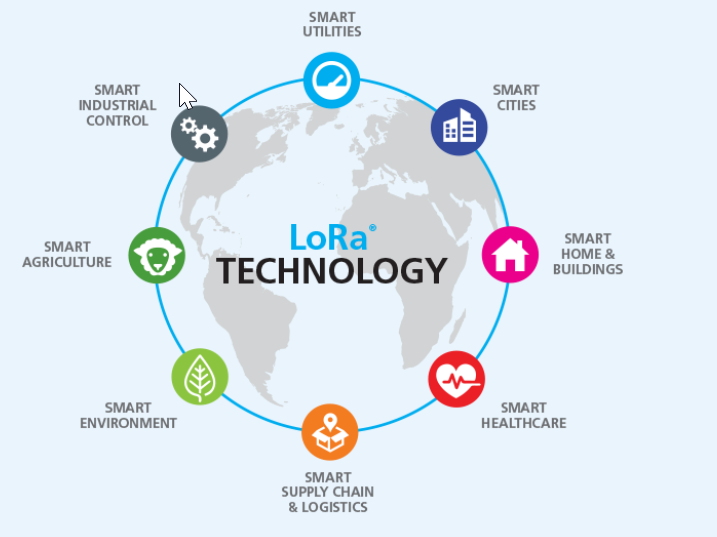
Why do smart factories need LoRa?
Smart factories focus on a data-driven approach to manage their facilities, improve processes and to spot any issues that may occur. It does this through interconnected networks of machines, devices and communication tools. LoRa and LoRaWAN can help smart factories become more efficient and productive thanks to their long range, low-power usage. Take a look below at a few of the many ways LoRa can improve and streamline everyday working processes:
Asset and facility monitoring
The use of telemetry and geolocation data in an industrial IoT solution provides a clear picture of how assets are working. For IT and operational technology environments, sensors improve insight into physical spaces. To increase operational effectiveness, reduce theft, and optimise logistics, geolocation data can be used to track and monitor assets and their locations.
Environmental monitoring
Temperature and humidity, closed/open door status, illumination levels, and occupancy can all be measured with LoRaWAN sensors. Private data is recovered using the LoRaWAN network and delivered to a SCADA system for visualisation and archiving.
Factory automation
Connecting Modbus data to a private LoRaWAN network will allow you to retrieve data from remote assets using intelligent sensors that may be kilometres away through solid obstacles like buildings, walls, and other solid objects. Eliminate manual data recovery methods and expensive cabling that frequently bring flaws into systems.
Smart industrial management
Sensors can be used to remotely monitor equipment and vehicles to manage resources. This includes electrical current testing, temperature readings, water metres, steam traps of heavy equipment like forklifts, trucks, diesel tankers and backhoes and concrete mixers.
Co2 level monitoring
Using LoRaWAN and LoRa-based CO2 sensors deployed in office buildings and workspaces, you can monitor ventilation, ensure there is sufficient natural light, manage noise levels, and enhance other elements of employee wellbeing.

Benefits of LoRa technology for smart factories
Different priorities are needed for each smart factory and smart manufacturing plant. As a result, the LoRa solution may be expanded to meet the requirements of various projects with the following advantages:
- Increase operational effectiveness.
- Make the workplace more ideal.
- Keep your carbon emissions low to protect the environment.
- Cost and energy savings.
- Recognize potential flaws and risks.
- Maximise the use of the personnel and resources.
Advantages of using LoRaWAN for smart factories
- Long broadcast range
- Low power consumption
- Low cost
- Remote configuration
- Wireless data collection without tangle wiring
- Tolerance of latency with suggested report interval
Recommended LoRa products
Seeed Studio LoRaWAN Gateway Module

Arduino Edge Control Kit
M5Stack LoRa Communications Module

ST LoRa Tracker and GPS Module Evaluation Board

SparkFun expLoRaBLE LoRa Thing Plus Development Board

Adafruit FeatherWing RadioFruit Board with LoRa Radio

FAQs
LoRa and Wi-Fi are used for different purposes. A brief comparison of these two technologies is as follows: Wi-Fi sends big volumes of data quickly over a short distance, but LoRaWAN sends little amounts of data several times an hour or day across distances of several kilometres.
The only communication channel that a LoRaWAN node requires is the LoRaWAN network. However, the gateway will need a cloud service, such as TTN (The Things Network).
LoRa transmissions can penetrate through metal, concrete and glass. This ability to penetrate through surfaces is why it can be advantageous over other networks like Wi-Fi.
In built-up areas, LoRa can reach up to three miles (five kilometres) and up to ten miles (15 kilometres) or more in rural settings.
Its long-range and deep penetration capabilities make LoRa an ideal solution for smart underground mining applications.











