With the rise of IIoT and other data collection technologies, there is an ever-increasing amount of data available for predictive maintenance. The challenge is how to effectively analyse this data to identify patterns and predict failures.
In the season of shutdowns, a lot of predictive maintenance activities will be carried out. This is the time of the year when warehouses and manufacturers close down so all machinery can be thoroughly checked. Now the inspection can be done more smoothly and efficiently. With new technologies, maintenance is simpler and more efficient.
Predictive Maintenance Innovations: AI, IoT, and Big Data
This is not the first time where we dedicate an article to advanced technologies in predictive maintenance. In the top trends reshaping industrial maintenance article we centred attention on AI, IoT, sensor technology, additive manufacturing and MaaS. Within these two years some things changed but still the focal point is concentrated on the same break-through technologies. Keep reading to find out what current trends are dominating the predictive maintenance sector to minimise downtime and avoid unexpected costs.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
With the current rapid advance of artificial intelligence (AI), there is huge potential to use it with predictive maintenance. AI influences pretty much all sectors and it is not new in manufacturing, it enhances the production in Industry 4.0 and becomes key in industry 5.0. It is also common in organisations’ security systems.
There is a growing interest in how these technologies can be used to analyse data, detect anomalies, and predict equipment failures. AI and machine learning (ML) enhance predictive maintenance by automating data analysis, detecting anomalies and early warnings, making accurate predictions, optimising maintenance schedules, providing decision support, and continuously learning and improving performance.
Predictive Analytics and Big Data
Thanks to more analytics, you can improve data processing. Big data technologies enable the storage, processing, and analysis of large volumes of data collected from various sources, such as sensors, maintenance records, and historical data. Predictive analytics techniques leverage this data to identify patterns, correlations, and anomalies, providing insights into equipment health and performance.
As per StartUs insights, big data platforms increase system health conditions’ transparency. This permits accurate modelling and successful predictions by looking for patterns in huge datasets. These data-driven forecasts offer insightful information that can help business choices be made more quickly and with more accuracy.
Industrial Internet of Things
Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), as a subset of a larger IoT, is another technology that is changing the way companies approach predictive maintenance. It concentrates on the specific needs of industrial applications like manufacturing, oil and gas, and utilities.
IIoT sensors in automated, IIoT-driven predictive maintenance systems may be used to find issues with a machine’s operating health, such as vibration, temperature fluctuations, or wear patterns on parts. Internal sensors can collect real-time data from machines and equipment, which can be used to predict equipment failure before it occurs.

Digital Twins
Digital twins technology is a growing sector in production and healthcare, but is also crucial in predictive maintenance. A digital twin is a virtual replica of a physical asset or system that simulates its behaviour, performance, and characteristics in real-time.
In predictive maintenance digital twins are a valuable tool for maintenance teams, helping them proactively manage assets, optimise maintenance activities, and improve overall asset performance and reliability. They provide real-time monitoring, predictive analysis, condition monitoring, anomaly detection, optimization of maintenance strategies, what-if analysis and simulation, training and knowledge transfer, and enable continuous improvement.
“The most common advantages across all digital twin applications are quicker risk assessment, predictive maintenance, real-time monitoring, better collaboration, and decision-making.”
Statista
Immersive Technologies
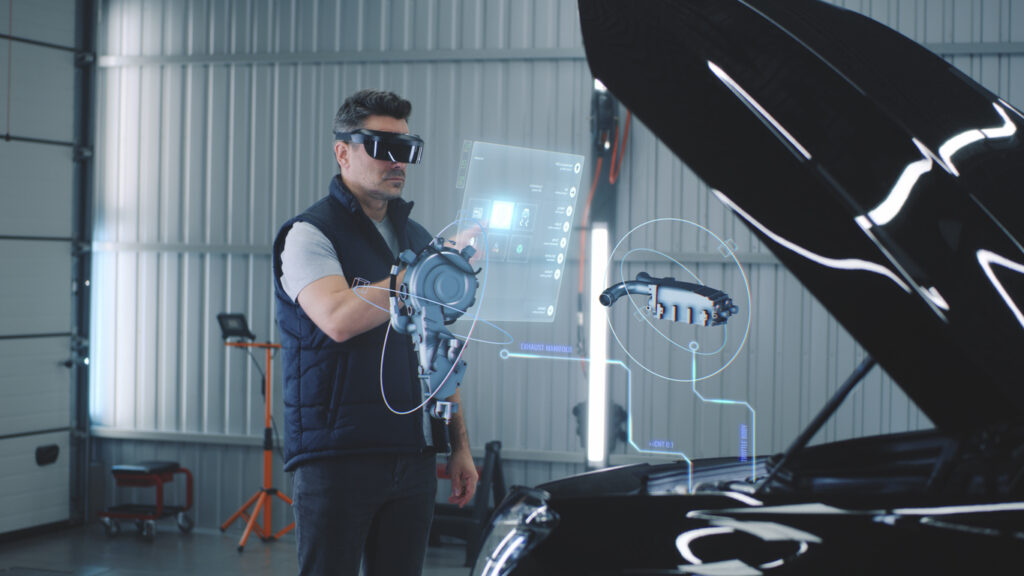
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) offer valuable benefits to predictive maintenance. The fact that now you can visualise mill repairs using wireless measurements, smart phones, smart glasses, and cloud computing drastically changes the way maintenance is performed. It opens up opportunities for immediate visualisation and repair of maintenance issues that are just starting, anywhere from the chip conveyors to the wrap line.
Immersive technologies can not only enhance predictive maintenance by enabling visualisation and simulation but also help with remote assistance, interactive maintenance procedures, immersive training experiences, remote equipment monitoring, integration with digital twins, and improved documentation and knowledge management.
The advances in predictive maintenance
With IIoT, AI and ML, big data analysis and digital twins, the future of predictive maintenance will be much easier. These trends enable organisations to move from reactive to proactive maintenance strategies and at the same time reduce costs, improve asset reliability, and enhance operational efficiency.











