It is essential to incorporate sustainable practices into every part of our life in a society where combating climate change and protecting the environment are major objectives.
Heating is one thing that has a big potential for lowering our carbon footprint. We can lessen our dependence on fossil fuels and help create a cleaner, greener future by switching to environmentally friendly heating solutions.
Whether you are replacing your HVAC system or you are looking for a completely new heating system, it is crucial that you take into account the impact on the environment. Newer heating solutions are better for us and the planet than traditional systems, like oil and gas-fuelled boilers. Discover the most innovative heating technologies that are eco-friendly and effective in this article.
3 Main Environmentally-Friendly Heating Systems
Thanks to renewable energy sources we can access heating from the ground (geothermal), the air (air-source heat pumps) or sun (solar thermal). Which are the most sustainable? Read on to find three low carbon heating options.
1. Heat Pumps
Heat pumps are effective energy-saving devices that transfer heat indoors from the air, the earth, or water. Although heat pumps need power to run, they can produce roughly three units of heat for every unit of electricity used, which results in huge energy cost savings.
“Accelerated deployment of heat pumps, in line with national climate targets, can reduce global CO2 emissions by half a gigatonne already by 2030.”
– International Energy Agency (IEA)
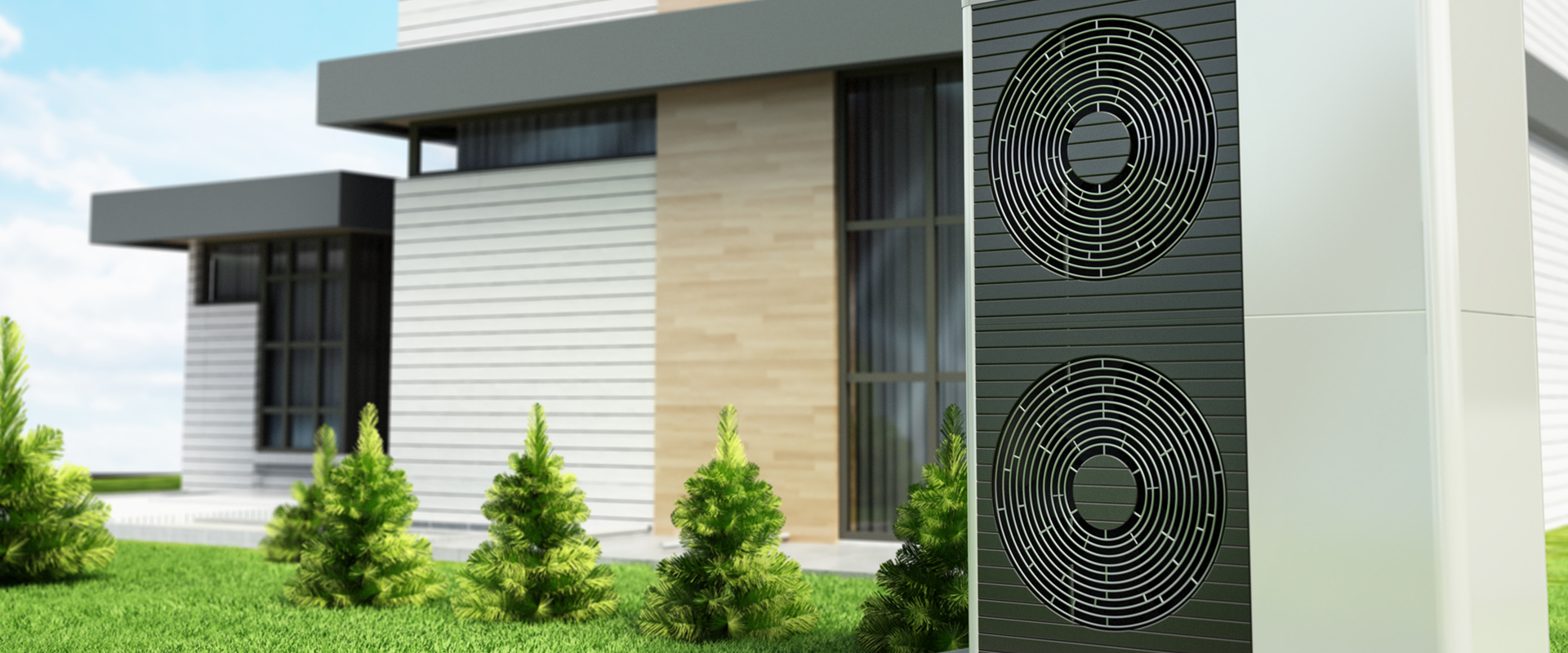
Air-Source Heat Pumps
Air-source heat pumps extract heat from the outside air and transfer it indoors to provide heating. Although the pump’s effectiveness might be slightly lower in cold temperatures, air-source heat pumps still draw heat from the outside air and deliver it into the house.
There are two different types of air source heat pumps that are either air to air pumps or air to water pumps. While the first one provides only space heating, the other provides both space and water heating.
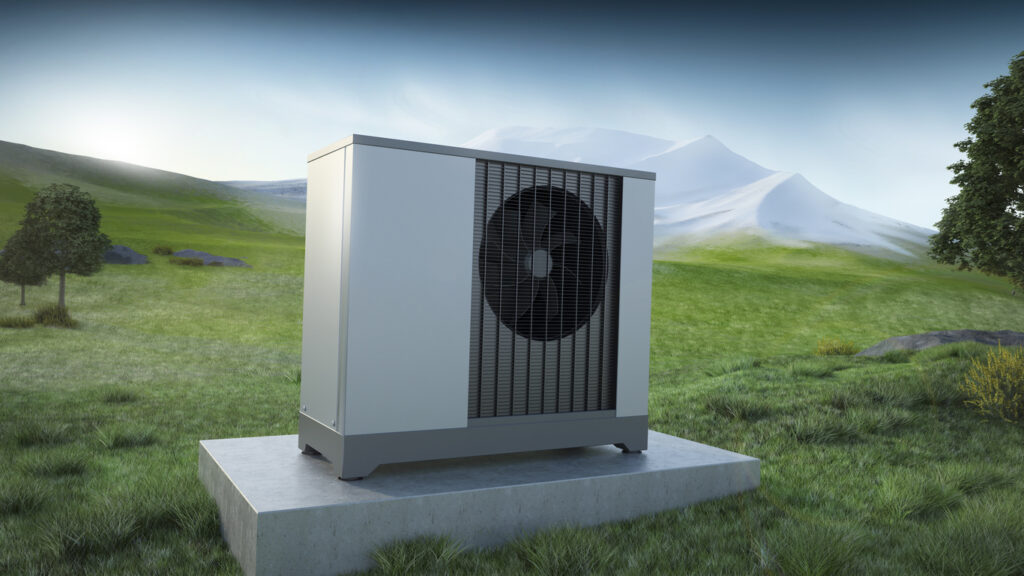
Most air heat pumps are made up of an indoor unit that disperses heat throughout the structure and an exterior unit that absorbs heat from the surrounding air. By removing heat from within and releasing it outside, air-source heat pumps can also be used in reverse to offer cooling during hot weather.
Air heat pumps are energy-efficient and have low running costs. It makes them ideal for those who want to cut their energy costs and contribute to a better environment.
Geothermal (ground-source) Heat Pumps
Ground-source heat pumps, commonly referred to as geothermal heat pumps, use the relatively constant ground temperature to produce heating and cooling. In essence, it is a constant temperature of the earth used to heat your home. Geothermal heat pumps are both an eco-friendly and efficient heating system.
How is the energy generated? Through underground pipes, ground-source heat pumps draw heat from the earth. The fluid transmits heat from the earth to the indoor heat pump system. Although geothermal heat pumps are more labour-intensive to install and relatively pricey compared to other forms of heat pumps, they are extremely efficient and can drastically cut energy costs.
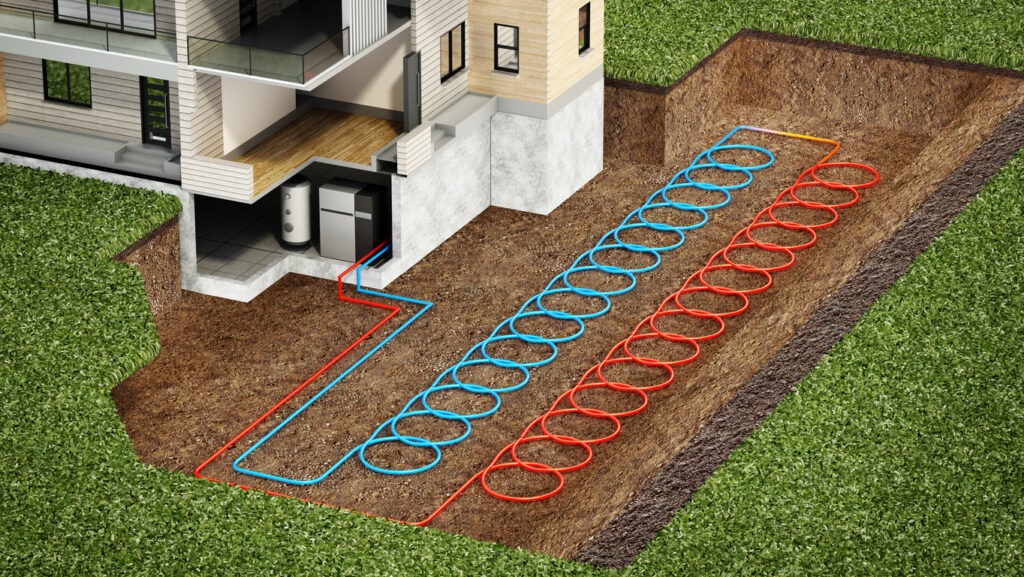
To find out more about geothermal energy, click here.
Water-Source Heat Pumps
Whether it is a requirement for heating or cooling, water-source heat pumps move water through a system of pipes that extract or release heat. These pumps employ local bodies of water, such as lakes, rivers, or ponds, as a heat source or heat sink. Water-source heat pumps are effective and capable of sustaining consistent performance independent of changes in the outside air temperature. But they need access to a reliable water source, which might not be available everywhere.
2. Solar Thermal Heating Panels
When it comes to solar heating, most people think about solar panels, which turn sunlight into electricity but there is a lesser known solar energy which can be used to provide domestic hot water. They are called solar thermal panels.
Solar thermal heating panels serve as the main component of these systems, capturing solar radiation and converting it into useful heat. These heating systems that use solar energy to heat water and air fall into two categories:
- Solar air heating systems – in this system air is heated directly by sunshine and then circulated throughout the building.
- Solar water heating systems – water heated by this system can be utilised to heat the house or for household hot water.
By utilising the natural power of the sun, solar heating systems provide an environmentally friendly and renewable heating solution. In addition to solar heating, photovoltaic (PV) panels are another technology that harnesses the sun’s energy. Solar panels are relatively easy to install and are an excellent source of energy for those looking to reduce their carbon footprint. Find out more about the solar photovoltaic (PV) panels installation.

3. Biomass Heating
The third environmentally-friendly heating system is biomass boilers, similar to oil and gas boilers but instead of burning fossil fuel they burn biomass materials such as wood pellets, agricultural waste or specially bred energy crops. Wood pellets are automatically fed to biomass boilers, reducing the need for frequent refilling. Logs and wood chips, which you may find for free, can be used in residential boilers.
Using this heating method, biomass can be burned effectively in boilers or furnaces to produce hot water and space heating. Biomass, as a naturally occurring fuel, is a renewable energy source that can be collected sustainably, unlike coal.
Conclusion
As per IEA, the role of efficient and low-carbon heating technologies continues to grow, but fossil fuels still meet over 60% of heating energy demand. Gas and oil are still the most commonly used to heat buildings.
Therefore, transitioning to environmentally friendly heating systems is a crucial step. With geothermal heating systems, solar heating systems, biomass heating systems, and heat pumps offering innovative and sustainable alternatives, they can easily replace traditional heating methods.
By adopting these technologies, we can decrease our reliance on fossil fuels, lower carbon emissions, and create a more sustainable future for generations to come. Embracing environmentally friendly heating systems is not only an investment in our planet but also in the comfort and well-being of our homes.












