Electric boards are essential in connecting various components and allowing them to communicate with one another. They are basically in every piece of electronics – our phones, sensors and other electronic components. In order to power these devices, there are complete circuits needed. To help create circuits with the right components RND is a brand that provides its customers with great value products.
A short introduction to Electronic Circuits
You probably know already that a printed circuit board (PCB), also called printed wiring board (PWB), is a typical electronics’ board base. They are designed for physically supporting and wiring surface-mounted and socketed components. Printed circuit boards can be single or multiple-sided. The more sides a printed circuit board has, the more it is complicated. Also multi-sided boards mean that the gadget has more power.
Many people compare PCBs with cities. You probably encounter the term, that circuit boards are like cities, that provide a complete system for all the electronic components that make our devices run. In essence, the printed circuit board is at the heart of every device and makes all electronic components come to life. Printed wiring board production has expanded throughout the years in order to meet the growing need for better, faster, and more complicated semiconductor technology. It is mainly to create more advanced devices and applications.
Industrial Applications of PCBs
PCBs are used in many industries, from small consumer devices through to medical devices and automotive equipment. At the same time, the industrial sector benefits greatly from printed circuit boards that are especially useful on production lines and in manufacturing plants.
Automated production lines help businesses save on costs and reduce human errors. However, electronic components in production often require additional high-powered PCBs that can survive in harsh environments and can handle vibrating machinery and extreme temperatures. Thus PCBs have to be specially built to handle high-power applications and the harsh conditions.
Examples of PCB usage in the industrial sector:
- Power equipment: power supplies, inverters, control devices, solar power equipment, etc.
- Manufacturing equipment: power drills, assembly machines, presses and ramps, and other PCB-based electronics.
- Measuring equipment: equipment used to control measurements like temperature, pressure and other variables in the manufacturing process.
Breadboards and Printed Circuit Board
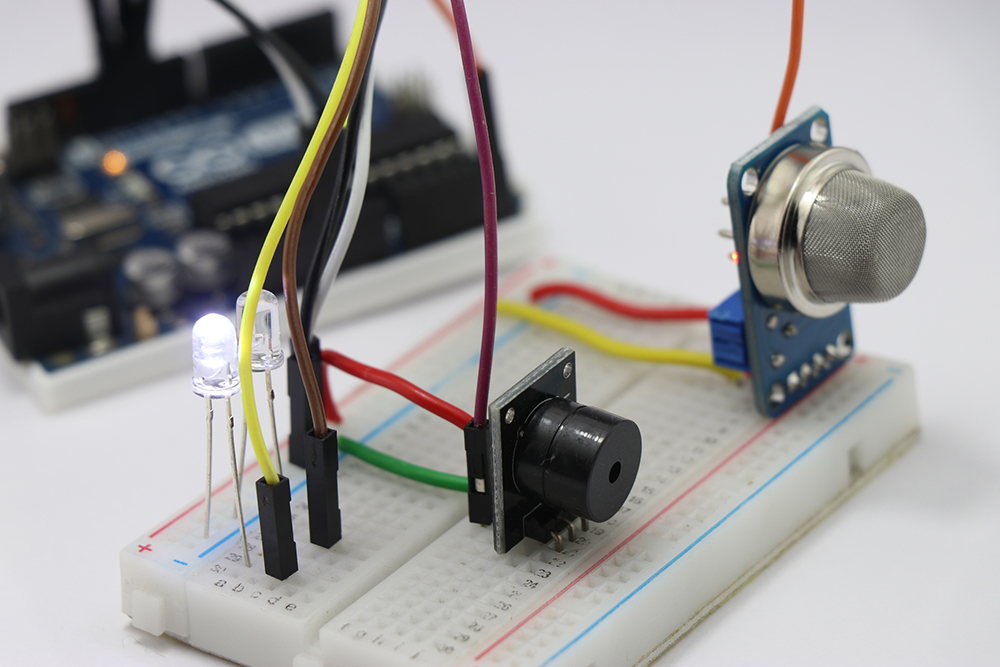
A breadboard is typically employed as the first step in the creation of a printed circuit board – the ‘bread’ so the base of the concept. Breadboards make it possible to create circuits without the need for soldering. These circuits are recommended for beginners but also suitable for electricians familiar with development boards but want to start large-scale projects.
The designer has to know what type of electronic board is the most sustainable for their project. It is probable that you will prototype the wiring on a breadboard when building a robot or any other electronic project. A breadboard is typically used in the initial stage before making a printed circuit board. A protoboard allows you to alter and move circuitry that would otherwise be permanent on a PCB. Breadboards are utilised for design and exploration, whereas boards are for your finished items. The rectangular plastic board has many holes allowing for the insertion of electronic components to prototype an electric circuit.
With the RND breadboards and jumper wires, you can find a solution, whether you want to prototype or check how the circuit reacts.
PCB Connectors
PCB connectors are the main and crucial part of evaluation boards. They transfer signals or power from one PCB to another or from another source within the device between the PCB. Connectors often require mounting, either through-hole mounting or surface mount. There are male and female PCB connectors, and they come in different sizes, shapes and unique attributes as well as vibration resistance, etc.
The main purpose of PCB connectors:
- Interconnections – a stiff or flexible link between two PCBs
- Cabling connection – bundled, wired connection for off-board devices
- Programming/debug connection – a connector (or test point array) used for debugging or programming, typically for a microcontroller or field-programmable gate array (FPGA).
Types of commonly used PCB connectors:
- Wire-to-board
- Board-to-board
- Male PCB Connectors/ Pin headers
- Female PCB Connectors
- Backplane Connectors
- USB connectors
- RCA Connectors
- Audio Connectors
- D-Sub Connectors
- Barrel Connectors
- RJ Connectors
- IEC Connectors
- Banana Connectors
- RF Connectors

IDC Connectors and Ribbon cables
You might need to transfer data between a ribbon cable and a printed circuit board (PCB). To do so, there are IDC connectors that are line-to-board connectors. Their primary role is to link one circuit board or subsystem to another. The connector includes a variety of safe and cost-effective connection methods that can establish a stable hermetic connection between the ribbon cable and the PCB.
RND IDC connectors and ribbon cables are built with your PCB specifications in mind. They are a simple and compact solution for every application.

Commonly Used Components on PCBs
There are numerous components required to keep your device working smoothly. All components ‘meet’ on the circuit board to create a fully functional electronic system with energy capacity.
Resistors
Resistors are one of the most often used PCB components – they are the foundation of current control. Their function is to obstruct current flow by releasing electric power as heat. Resistors exist in a variety of styles and materials. The most common type of resistor is one composed of carbon film. Typically, axial resistors have leads attached to the ends of the two sides of the rod. Also there are coloured rings, or also called bands, on resistors that provide the colour coding. These rings are code that represents the resistance value, the tolerance, and, occasionally, the dependability or failure rate. The number of bands ranges between three and six. At the very least, two bands represent the resistance value, while one band acts as a multiplier.
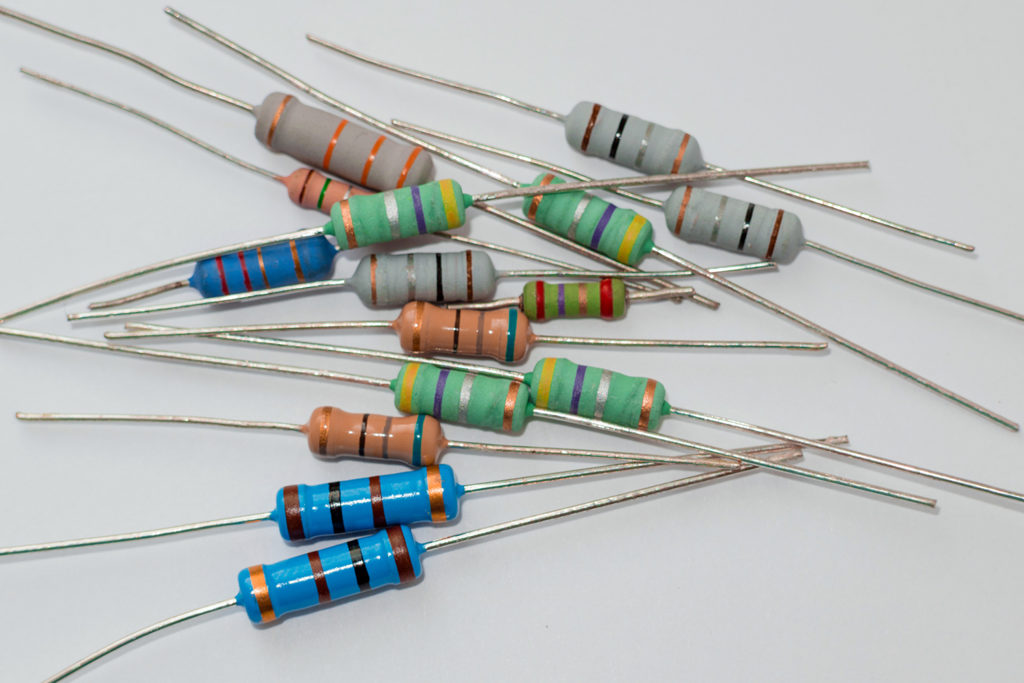
Transistors
Resistors are essential for current management, but transistors are essential for all modern electronics. They are, in reality, the building blocks, so they are nothing more than amplifiers and electronic switches. They are classified into three types, the most common of which is the bipolar transistor (bipolar junction transistors: BJTs). This transistor has three components and three pins that allow current to flow and amplify. The second type is field-effect transistors (FETs) that is a unipolar device with no pn junction in the primary current path. In addition, two types of field-effect transistors are produced: N-channel and P-channel. Lastly, the third insulated-gate bipolar transistors (IGBTs), made up of a voltage-driven MOSFET (metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor) followed by a high-current transistor.

Capacitors
Capacitors can be found on every PCB board. Capacitors store energy and release it when additional power is required elsewhere in the circuit. They are kind of small batteries with even smaller storage space and the ability to lose and acquire energy over very short period of time. As a result, they are frequently employed as a backup source of energy to prevent data loss when the primary source of power fails. Capacitors are classified according to the conductive material of the plates or the insulating material that separates them. Polyester capacitors, ceramic capacitors, or radial capacitors are commonly used by novices and casual hobbyists. To distinguish capacitors from resistors, keep in mind that capacitors have two leads that protrude from the same location.

Inductors
Inductors, also known as coils, chokers, and reactors, are typically made up of an insulated wire-wrapped core. They, like capacitors, play a significant role in energy storage. However, whereas capacitors use an electrostatic field, inductors employ a magnetic field to store energy. When energy passes through them, a magnetic field is created. The more times the wire is wrapped around the core (i.e., the number of windings), the stronger the magnetic field and thus the energy is generated. The windings play a key function in strengthening the magnetic field, which has a significant impact on the stored energy.
Diodes
Diodes are incredibly important on a printed circuit board.. These two-terminal components regulate and divert energy flow by allowing current to flow in one direction while blocking it in the other. They rely on the electrical resistance theory to perform properly. This enables them to exert control over the flow of energy.

Batteries
Widely utilised batteries a common method to power devices that people use every day. However, they are also used as energy-supplying components in PCBs. Batteries work by storing chemical energy and converting it into electronic energy, which is then utilised to power various circuits on a printed circuit board.
Integrated Circuits
Integrated circuits (IC) are the brains of all printed circuit boards. They are widely used in electronic devices. Although batteries are a source of energy, circuits are power plants. Thousands (or even millions) of transistors, resistors, and capacitors are housed on these small wafers. As a result, they can perform numerous functions. They can have many energy operations taking place on a printed circuit board. Silicone is a material used in the fabrication of integrated circuits. There are two kinds of integrated circuits: digital and analogue.

Oscillators
Oscillators are electronic clocks that can be programmed. They are useful in many applications, e.g. quartz timepieces and audio and video systems. On printed circuit boards, oscillators are programmable timers or clocks that generate electronic signals. They also come in a variety of forms, including crystal oscillators that are utilised as precise timers in wristwatches, microcontrollers, and other similar devices. Others are Clapp oscillators, voltage-controlled oscillators, and many more. Oscillators can also be categorised based on several parameters. They could, for example, be based on a feedback mechanism.
Switches and Relays
The switch is a simple component that controls the current flow in the circuit by switching between an open and a closed circuit. Toggle switches, micro switches, rotary switches, and box-type switches are the most prevalent types of switches. They act as switches and can also magnify minor currents to produce bigger currents. Similarly, a relay is an electromagnetic switch that is activated by a solenoid, which acts as a temporary magnet when current runs across it.

Sensors
Sensors are electronic components that “sense” physical input or environmental changes and react accordingly. There are several sensors for diverse environmental stimuli, such as humidity, light, air quality, touch, sound, moisture, and motion. Sensors on printed circuit boards often convert physical energy to electrical energy. They can range from a type of resistor in a resistance temperature detector (RTD) to LEDs that detect infrared signals, such as those seen in television remote controls. Sensors are employed in a variety of practical applications, including humidity monitoring, air quality detection, motion sensors, and controlled lighting.
Designing PCBs with the right electronics
Designing for PCB connections is entirely dependent on the application, and it typically begins with the user’s needs. However, whether it is a design that will be produced on a mass scale or just an individual improvement, proven equipment and the right components are crucial to make sure the signal flow runs smoothly and without interruption through the PCB.
As you can see, RND provides an exhaustive range of components that will help you start with electronics design or will just fulfil any of your projects, offering affordable prices and high-quality.










