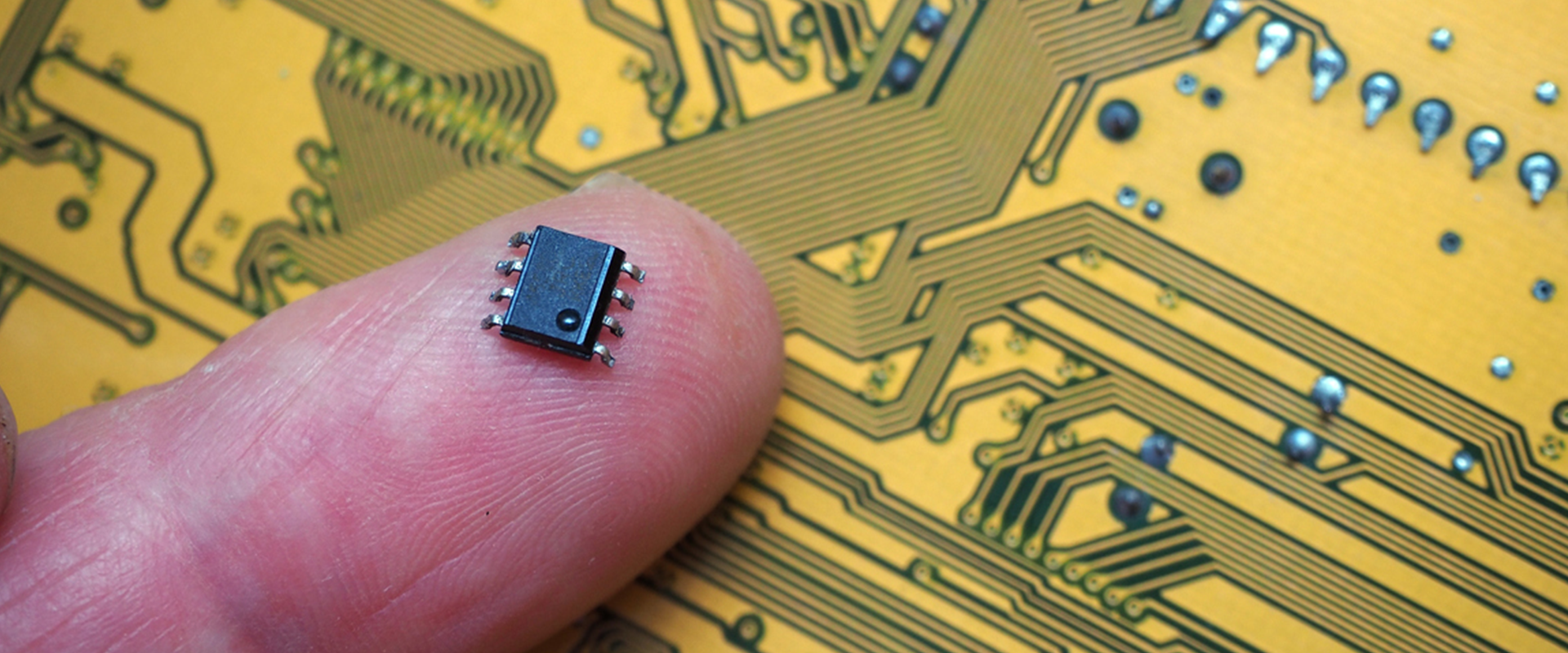
Advancements in technology have led to significant transformations in the electronics industry, allowing for smaller and more sophisticated products to be manufactured.
Miniaturisation has been one of the key factors in the development of electronic components enabling creation of smaller and more portable devices. From medical devices and wearables to autonomous vehicles and IoT sensors, the miniaturisation of electronics is set to play a significant role in shaping the future of technology.
Advanced electronics are crucial to many industries, and their manufacturing and production continues to shrink in size, allowing for more compact designs without losing power. Therefore, it is essential to implement efficient and cost-effective production methods, utilising extensive engineering expertise. With RND‘s assistance, you can seamlessly transition from prototype to production and develop the next disruptive electronic device – regardless of how intricate or compact the electronics may be.
Miniaturisation trend – how are components even smaller?
The world of electronics is constantly evolving, and one of the major drivers behind this evolution is the miniaturisation of devices. From the vacuum tube-triode to the contemporary transistor, components are becoming tinier. Starting from already crammed integrated circuits (ICs) with billions of transistors that are less than a nanometer in size, but crucial, as the miniaturisation of electrical devices involves more transistor nodes fitted into a smaller integrated circuit. Once the system is put together, the IC is interfaced within the system or device for which it was built so that it may carry out the intended purpose.
Miniaturisation is a process of overcoming obstacles and design limitations; it can transform the world of electronics as the possibilities are endless. Thanks to advanced manufacturing techniques, materials, and design methods, more functionality can now be integrated into smaller spaces than ever, without decreasing the strength. Even though the components are small, they are still really powerful.
Benefits of components miniaturisation
By miniaturising components you can benefit from:
- Increased efficiency
- Lower costs
- Increased portability and enhanced reliability
- Reduced power consumption
- Improved performance
- New opportunities: it has enabled entirely new applications and designs (more portable, powerful and affordable) which were impossible due to size and weight limitations before.
Advancements in electronics miniaturisation
Currently, not only well-known devices, like watches or smartphones are smaller but also their hearts, meaning circuit boards (PCBs). PCBs that connect electronic components have also shrunk in size. Thus more components can be fitted into a smaller space thanks to advancements in specialised system-on-chip (SoC) components, smaller passives and increased transistor density in potent processors, which we mentioned earlier. This has made it possible for newer devices to have more functionality that would previously have required multiple boards in a single package or multiple devices connected together.
Additionally, artificial intelligence (AI) and nanotechnology strongly enhance the miniaturisation trend. Engineers can design more complicated and advanced products by integrating AI and nanotechnology into component miniaturisation, among them are influenced data processing, materials research, and improved human-machine interaction. Other technologies, like IoT or 5G, which are common in our everyday devices as well as medical and portable computers, now also rely on smaller but yet more powerful computing systems.
RND miniature components
No electronics can work without the right components. Switches, sensors, semiconductors, passive components, connectors, are just some examples of modules which can be found in modern electronic devices. Often, they have to be thin and very small to fit wearables, robotic or automated systems, or even smart devices such as smartphones. Yet, even though they are smaller they are still packing the punch. RND has a vast array of miniature components in stock which can suit your project. Have a look below at the showcased examples and start your design right away!
Sensors
In the field of nanotechnology, miniature sensors are fundamental. With their various features, including exceptional electrochemical, photonic, and magnetic capabilities, size-affected nanomaterials become appropriate materials for sensing. The combination of AI algorithms with nanoscale sensors and actuators open up new opportunities. This may make it possible to develop intelligent, self-adaptive systems that can react to their surroundings in real-time without requiring outside direction or control.
The RND level sensors with IP67 rating are one of the smallest on the market. The brand’s miniature sensors are perfect for water dispensers, tank monitoring systems, vending machines, coffee makers, and printing equipment. Some from the series have polypropylene housing, which makes them appropriate for a variety of applications, even interaction with food.
Toggle Switches

In order to switch an electrical circuit, toggle switches include an operating lever that can be moved up and down or left and right. Put simply, it is a digital on/off switch. The best usage for toggle switches is to change the status of system settings and functionalities. To allow users to select between two opposed states, toggles may be used in place of two radio buttons or a single checkbox.
RND has miniature toggle switches with a 10.4 mm high actuator, ideal to use with circuit boards. These switches have a small footprint, are incredibly sturdy with low contact resilience and are very easy to seal.
Circular connectors
Circular connectors with many pins are often used for exterior connections. They can be used to convey electrical signals, power electrical devices, or transport data. The miniature ones are frequently used in industrial and automotive settings. They are especially helpful for communications that employ low voltage and low signal.
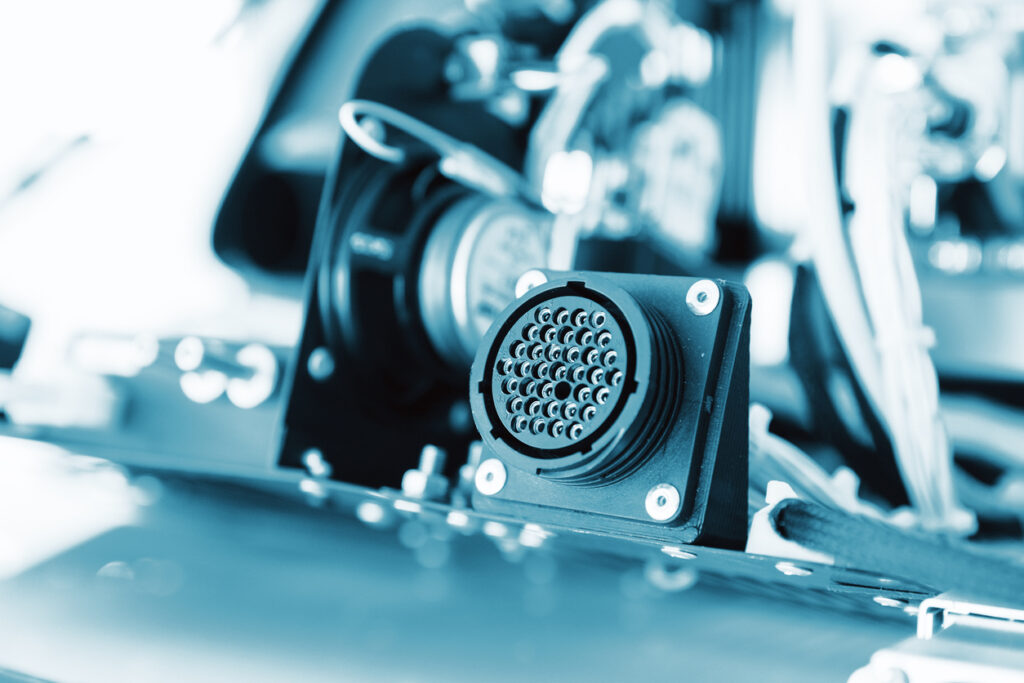
Miniature circular connectors from RND are available in a range of sizes and are built to last and to save both weight and space. The variety of types enables you to make the optimal decision for an application’s space requirements as well as other requirements for high-speed, tough applications. RND offers high-performance connectors made with space-saving and severe environment requirements in mind.
Speakers
A speaker is an electro-acoustic transducer that converts an audio signal into the matching sound. Small loudspeakers known as miniature speakers are made for products with restricted product diameters. Miniature speakers are low-profile, compact, and equipped with either paper or mylar cones.To function, they often require an external drive circuit.
Their applications include radios, headphones and headsets, computers, electronic musical instruments, and handheld applications. They are useful in equipment where having a high-quality sound is important as well as when longevity is required.
RND offers miniature speakers in various power ratings, as well as in various shapes, round or rectangular, encased with leads and connectors.
Neodymium magnets
Neodymium magnets are manufactured from an alloy of the metallic elements neodymium, iron, and boron and are permanent magnets (i.e., they produce their own magnetic field). They are currently the strongest permanent magnets available on the market. They provide unequalled levels of magnetism and demagnetization resistance when compared to ferrite, alnico, and even samarium-cobalt magnets. Their maximum operational temperature is typically 80°C. Neodymium magnets have a wide range of applications, however caution is advised because they are fragile, do not bend, and could collide and break.
The future of miniaturisation
Since the invention of the first transistor in the late 1940s, the trend towards miniaturisation has grown and is present in many industries. The electronics, automotive, 3D printing, medical, and lab industries, as well as material technology research, mechanical design, and manufacturing processes, especially in IIoT and Industry 4.0, will undoubtedly benefit more from miniaturisation over the next ten years as technology advances towards smaller, more reasonably priced, and more effective devices.