In the dynamic world of electronics, there are newer and better innovations, from a miniaturisation trend to faster and more efficient devices. Electronics are a fundamental part of modern devices and equipment. They all produce electromagnetic fields that have the potential to cause electromagnetic interference (EMI). This is where electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) comes into play.
EMC, together with Bluetooth have revolutionised connectivity and ensured the safe operation of electronic devices. Bluetooth has driven the standardisation and adoption of Bluetooth technology since the late 1990s and has become a ubiquitous wireless protocol, integrating with devices from smartphones to industrial systems and smart home appliances. Meanwhile, EMC ensures reliable, interference-free operation of these devices, safeguarding performance and preventing disruptions.
This article explores the intricacies of Bluetooth and EMC, detailing their history, technological advancements, and practical applications, highlighting their essential roles in modern electronics.
The Origin of Bluetooth: Connection of Devices
The history of the name “Bluetooth” begins with Danish king Harald “Bluetooth” Gormsson, who lived in the tenth century. Bluetooth’s name comes from his unusual blue-tinged tooth, which came to represent his capacity to bring the kingdoms of Denmark and Norway together. The basic goal of Bluetooth technology, to harmonise communication across various electronic devices, is a reflection of this history, just as Bluetooth’s namesake monarch brought various languages and civilizations together.
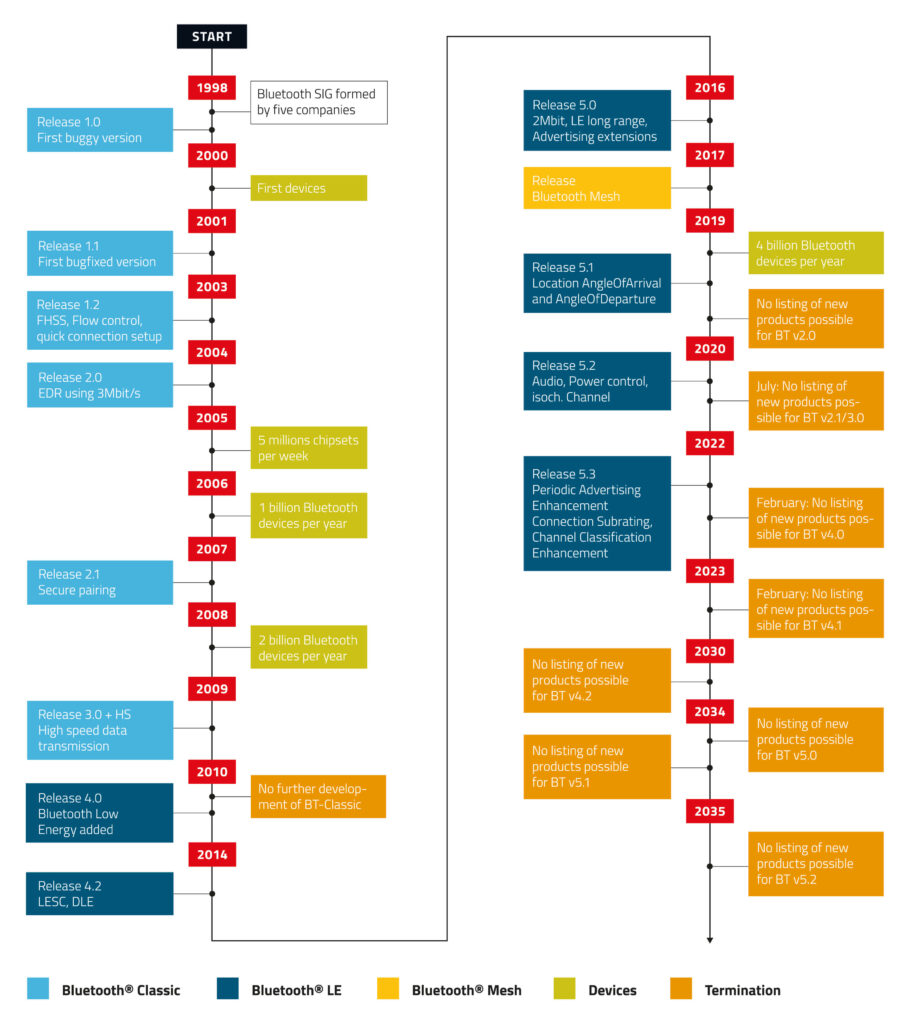
The Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG), formed in 1998 by a consortium of industry leaders including Intel, Ericsson, and Nokia, set out to standardise this short-range radio technology and enable seamless connectivity across a wide range of products and industries. With Bluetooth, it is possible to connect a wide range of devices and use it for everything from industrial automation to wireless audio streaming.
The Evolution of Bluetooth Standards: From Classic to Low Energy
Bluetooth technology is constantly expanding and in 2024, it will have advanced enough technical features to be used in even more products and applications, including broadcast audio, wireless sensors, and real-time location and tracking systems. Since its beginnings, Bluetooth technology has evolved remarkably, with new features and capabilities added to each iteration. Wireless connectivity was made possible via the early Bluetooth Classic standard, which was released in version 1.0 and allowed for data transfer and music streaming between compatible devices.
Bluetooth Low Energy (LE) was released in version 4.0 in response to the growing demand for energy-efficient wireless solutions. Bluetooth LE prioritised low power consumption while ensuring dependable data transfer, keeping the Internet of Things (IoT) in mind during its design. In order to enable more flexible and focused applications, this version also added important features like GATT (Generic Attribute Profile) and a number of device roles, including Broadcaster, Observer, Peripheral, and Central.
The capabilities of the technology were further enhanced and expanded by later Bluetooth LE versions. Upgrades to version 4.2 included enhanced coexistence with 4G networks, secure pairing, and longer data length. More advanced advertising features, increased throughput, and a longer range were brought about by Bluetooth 5.0, which opened the door for more complex IoT applications and wireless music solutions. For instance, Proteus-e and Proteus-III from Würth Elektronik are two notable modules that use Bluetooth 5.1 for better performance, longer range, and high-throughput data transmission.
Bluetooth Certification and Qualification Process
The Bluetooth SIG oversees an incredibly rigorous certification and accreditation procedure, which is a primary factor in ensuring the interoperability and reliability of Bluetooth-enabled products. Manufacturers must navigate a complex and demanding process that includes qualification, declaration, and listing to demonstrate compliance with Bluetooth specifications.
Under the strict supervision of Bluetooth Qualification Consultants (BQCs), a device or module must undergo extensive testing to confirm it meets the Bluetooth SIG’s technical standards. This rigorous testing process, which includes assessments of radio frequency performance, interoperability, and conformity tests, ensures the product can consistently communicate with other Bluetooth-certified devices, preserving the integrity and coherence of the Bluetooth ecosystem.
After qualification, manufacturers face the daunting task of completing the declaration and listing process by submitting the necessary data and documentation to the Bluetooth Special Interest Group. This formal registration, which grants permission to use the Bluetooth trademark, is crucial for enhancing the device’s interoperability and compliance but can be a significant hurdle for many manufacturers.
Thankfully, Würth Elektronik is here to ease this arduous process. As the go-to expert, Würth Elektronik ensures that its Bluetooth-enabled products meet all necessary standards, streamlining the certification process, reducing time-to-market, and simplifying development. With Würth Elektronik’s unparalleled expertise and support, overcoming the stringent requirements of the Bluetooth SIG becomes a seamless experience, making market entry smoother and more efficient.
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC): Ensuring Safe and Interference-Free Operations
In addition to Bluetooth technology, Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) has become an increasingly important subject in modern electronics. Ensuring that electronic equipment can function in their intended electromagnetic environment without producing or being impacted by EMI is the main goal of EMC.
EMC ensures that electronic systems may be effective and without interference in today’s electronic ecosystem, where communication is widespread and gadgets are becoming more integrated. Thus, the key is to confirm that one device does not inadvertently damage other devices and does not obstruct other devices concurrently. Uncontrolled electromagnetic emissions from one device can cause data loss, malfunctions, or even safety risks when they interfere with another’s ability to function. To reduce these dangers and guarantee the electromagnetic compatibility of electronic equipment, organisations such as the European Union and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) have developed EMC standards and regulations.
EMC Compliance: A Regulatory Requirement
The commercialisation of electronic items is now contingent upon EMC compliance in numerous regions. Strict guidelines and standards have been established by regulatory bodies, such as the EMC Directive, the European Union’s CE marking, and the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) in the United States, that manufacturers must follow before their products can be sold.
Adherence to these electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) standards guarantees not only the secure and dependable functioning of electronic gadgets but also the protection of the surrounding electromagnetic field. EMC compliance reduces the dangers associated with electromagnetic interference, which in turn benefits public health and safety by preserving the integrity of communication networks, vital infrastructure, and delicate medical devices.
The Importance of EMC
Electromagnetic interference is a possibility that rises with the number of electrical gadgets. This is especially true in the context of IoT, where a wide range of networked devices—from industrial automation systems to smart household appliances—need to coexist and communicate with each other in a seamless manner without interfering with their ability to function.
EMC makes sure that these gadgets can function in their intended electromagnetic field without producing unwanted electromagnetic effects or being impacted by them. This covers controlling radiation and conducted emissions as well as protecting electronics from outside electromagnetic interference. Manufacturers can guarantee the safety, dependability, and compatibility of their goods with the larger ecosystem of electronic equipment by following EMC regulations.
The Bluetooth and EMC: A Faster Market Entry

The field of EMC and Bluetooth have a mutually beneficial partnership that contributes to the development of a more secure and connected world. EMC compliance is more important than ever as Bluetooth technology develops and becomes more widely used. These two technologies have revolutionised industrial automation and smart manufacturing. Furthermore, with EMC products and Bluetooth it is possible to enter the market faster with fewer complications.
The growth of Bluetooth technology and the significance of EMC can be attributed to the IoT. From industrial automation systems to smart home appliances, Internet of Things gadgets depend on wireless connectivity. Widespread adoption of the IoT has been made possible by Bluetooth’s creation of low-power, energy-efficient Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) standards. These systems run consistently and safely without electromagnetic interference when EMC requirements are followed.
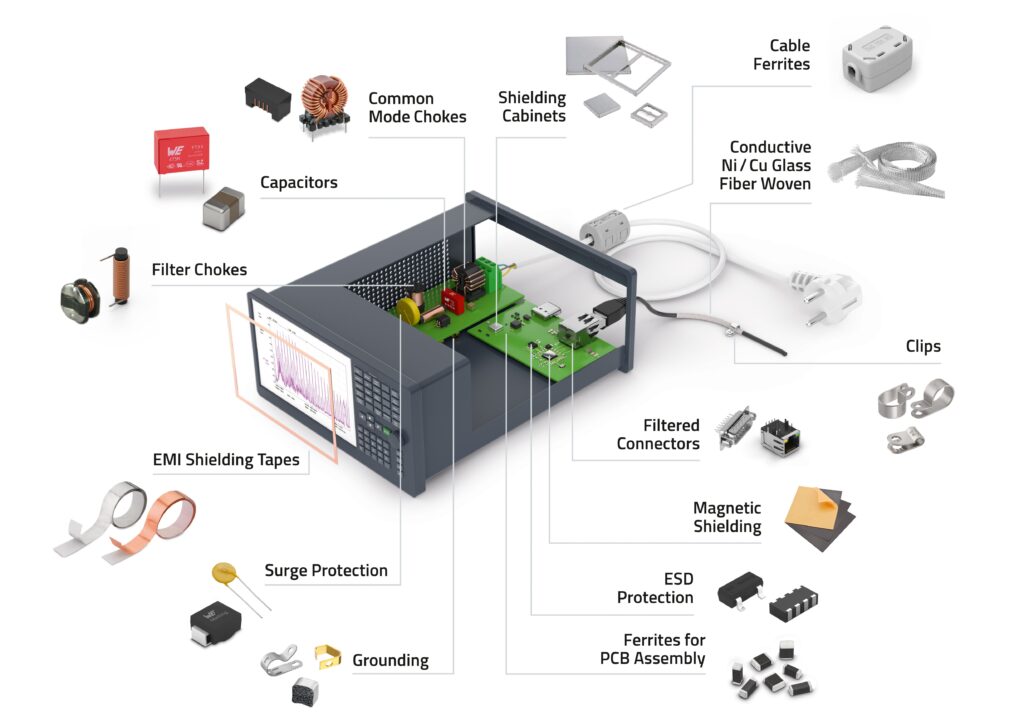
Würth Elektronik provides a wide range of Bluetooth-enabled devices, from Bluetooth modules to other, such as shielding and suppression materials, including EMI suppression ferrites that are designed to meet the needs of the embedded system market and split ferrites for cables (see the full range in the picture below) to satisfy various customer demands. These systems operate safely and dependably because of EMC regulations, which guard against equipment failures, downtime, and safety risks in mission-critical settings.
The Future of Bluetooth and EMC
As electronics and technology evolve, Bluetooth and EMC will play crucial roles in shaping the future. Emerging technologies like 5G, AI, and advanced wireless protocols make seamless connectivity and electromagnetic compatibility more vital than ever.
5G introduces new challenges in electromagnetic compatibility. Operating across wider frequency bands, 5G interacts with existing systems, including Bluetooth. Bluetooth’s collaboration with 5G partners is essential for ensuring Bluetooth devices function seamlessly in a 5G environment. AI and the “intelligent edge” underscore the need for reliable, low-latency wireless connectivity and electromagnetic compatibility. AI-driven edge computing demands real-time data processing. The Bluetooth’s advanced features, like Isochronous Channels and Adaptive Power Control, support low-latency requirements, while EMC compliance ensures safe operation without disruption.
The tech landscape is witnessing new wireless protocols like Ultra-Wideband (UWB) and Wi-Fi 6E. Bluetooth adapts by collaborating with these technologies, ensuring seamless integration and coexistence. Maintaining EMC and interoperability is crucial for a cohesive, interference-free user experience.
Embracing Bluetooth and EMC Synergy with Würth Elektronik
Bluetooth and EMC are essential partners in the evolving electronics world. Their synergy drives Bluetooth adoption, ensuring reliable and safe operation across diverse applications. As the demand for seamless connectivity grows, the importance of Bluetooth and EMC will increase. By addressing electromagnetic compatibility challenges, they are paving the way for a future of ubiquitous, secure, reliable, and interference-free wireless communication.
Through their collaboration, the Bluetooth and EMC experts empower manufacturers, developers, and users to harness Bluetooth technology’s full potential and the broader ecosystem of connected devices. As we embrace the future, Bluetooth and EMC will guide us towards a more connected, efficient, and technologically advanced world.
Manufacturers may concentrate on their core skills while making sure their products meet Bluetooth and EMC specifications and work flawlessly with other devices by utilising Würth Elektronik’s experience. Würth Elektronik helps customers realise the full potential of Bluetooth and EMC by guiding the way towards a more connected, efficient, and technologically advanced world.










