In our increasingly connected world, patch cables are all around connecting networking components over a short distance, they can be seen protruding from the back of the computers to wall plates and sprouting up to reach neighbouring hubs or switches.
A patch cable is so called because it is the plug and play version of Ethernet cabling as it is supplied with the connectors already in situ making it an easy and quick way to connect devices over a short distance.
The RND Patch Cables can help improve performance, speeds, with less interference and aid greater bandwidth for these short distance connections. Whether you need the cable for the office, home office or server rooms, RND has all the reliability your network infrastructure may require.
There are many different types of cables to choose from, but before embarking on any installations, it is crucial to address the specific requirements: such as required network configuration along with the amount of devices to be connected to ensure you maximise performance, safety and signal strength.
The modular nature of patch cables may appear to imply that their use is universal. However, there are some significant differences in the wiring configurations and connector pins. Hence why it is crucial to choose the right type.
Different Categories of Patch Cables
The cables are flexible and are grouped as seen in the below table depending on their maximum data transfer rate and bandwidth. The most common and widely used are that of CAT5, CAT5e and CAT6.
Each of the cables come with an 8P8C connector plug on each end for connecting two corresponding 8P8C jacks. The 8P8C connectors used in Ethernet systems have been called RJ-45, an FCC name for a Registered Jack with a similar 8P8C structure, due to the design’s resemblance to telephone cabling systems.
| Cable Type | Shielding | Transmission | Frequency | Connector Type |
| CAT 5 | Unshielded UTP | Maximum transmission speed of 10/100Mbps | Maximum bandwidth of 100MHz | RJ45 |
| CAT 5e | Unshielded UTP Single Shielded S/UTP Double Shielded SF/UTP | 1000 Mbps/1 Gbps | 100 MHz | RJ45 |
| CAT 6 | Single Shielded S/FTP Unshielded UTP | 10000 Mbps/10 Gbps | 250MHz | RJ45 |
| CAT 6a* | Double Shielded SF/UTP | 10000 Mbps/10 Gbps | 500 MHz | RJ45 |
| CAT 7* | Shielded only | 10000 Mbps/10Gbps | 600 MHz | Non-RJ45 |
| CAT 8* | Shielded only | 25 Gbps or 40Gbps | 2000 MHz | Class I: RJ45 Class II: Non-RJ45 |
5 Factors to consider when choosing a Patch Cable

- Shielding: shielding is used on some patch cables to help prevent electromagnetic interference from other sources. S/FTP and SF/UTP are shielded cables, while UTP cables have no shielding. Instead, wires are twisted to help reduce electromagnetic interference. UTP (Unshielded Twisted-Pair) cable is used in most Ethernet patch systems. UTP cable comprises eight insulated copper-core conductors twisted together in four pairs along the length of the cable.
- Speed: this is how much data a cable can transmit in a second. Cables are given category designations relating to how they can transmit data. An important factor to remember is the number of users can slow down the data so upping the cable category may help negotiate this.
- Cable length: there are a wide range of lengths available from RND from 0.5M to 20M. When measuring the length of cable required always remember to add in some slack, and the shorter the length the signal has to be carried and the less interference it will have.
- Location: where the cable will be run will determine what kind will be the best concerning the application. Cables have jackets, and different material types (e.g. PVC, PUR, polyamide) are needed depending on where they will be used, e.g. outdoors or on walls.
- Colour: the colours have been designed to aid quick network identification of the CAT cables use in the configuration, e.g. all the CAT5 cables are blue where the CAT5e cables are red etc etc.
An alternative to coloured cables is to use RND jacket colours. The jackets come in, blue, green, red, white and yellow. Such colour coding of cables may occur more widely in commercial situations, whereas more neutral black and grey options are common in domestic appliances. Depending on the type of shielding, explore the Cat 6 S/FTP Patch Cables range or Cat 6 UTP Patch Cables range.
Further specification information

CAT 5 & CAT 5e
Along with the general Cat5, there is Cat5e. The only difference between Cat5 and Cat5e is that Cat5e has a 1,000 Mbit/s throughput capability. They are also known as Gbit/s.

Features:
- Prepared cable with a screened RJ45 plug on both ends
- Connection cable for a structured building cabling
- Contact settings 1:1 under EIA/TIA568
- Complete screening aluminium laminated foil with additional braided shield (apply only to S/FTP patch cables)
- Construction: internal line 8 wires (apply only to UTP patch cables)
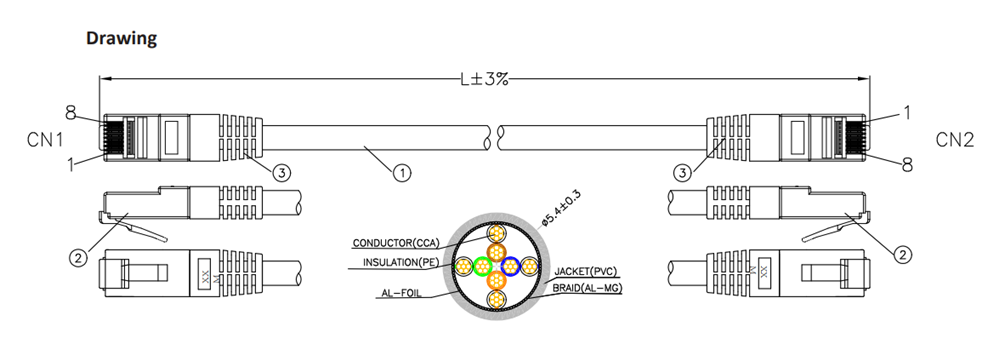
RND offers patch cables from category 5e in different lengths. The shielded with foiled twisted pairs (S/FTP) are long, from 1m to 20m. The unshielded twisted pair (UTP) have lengths from 500mm up to 5m. Explore CAT 5e S/FTP CablePatch Cables or CAT 5e UTP Patch Cables.
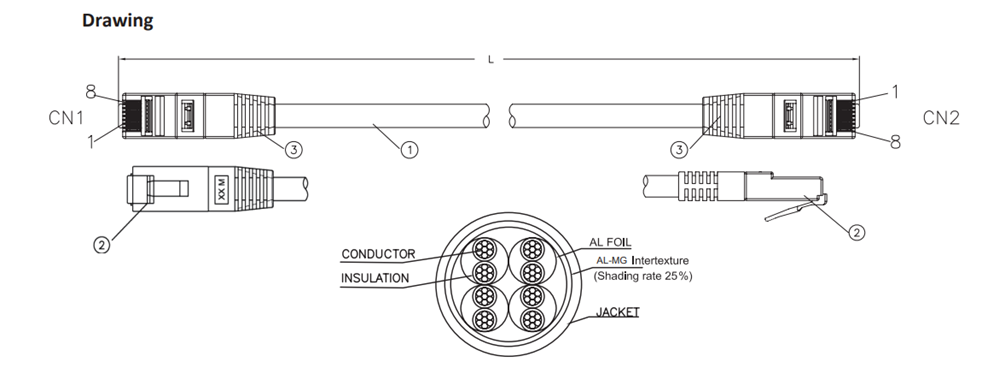
CAT 6
Category 6 is a twisted pair cable backwards compatible with Ethernet and other network physical layers with Category 5/5e and Category 3 cable specifications. Cables from Cat6 perform up to 250 MHz compared to Cat5e, which is more than twice that of Cat5e cables. These cables can transmit data at up to 10Gbps across up to 55 metres. Making them the ideal choice for a large number of users sending data at the same time.
Cat6 and Cat6a can often be the best solution for commercial buildings. That would be far too much for practically all home users. Cat6 cables, on the other hand, can be perfect for a quick and fluid network with sufficient bandwidth for a large number of users sending data at the same time.
CAT 6 S/FTP and UTP Patch Cables
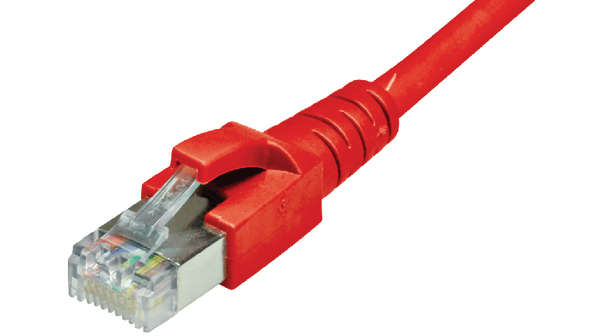
Features:
- Perfect for networking connections between device
- Suitable for narrow bending, flexible
- Twisted Pair cable, unshielded, includes RJ-45 connectors on both ends
- Durable due to moulded kink protection
Sometimes, different applications require different colours of your cable, especially when numerous types of cables are being used. It can be a way to differentiate and identify the cables, helping to keep track of the system configuration.
CAT 7
Category 7 is one of the higher performance cables and offers better shielding. It may be the best option when creating a core infrastructure. Choosing the right one to meet the system’s requirements will directly affect the performance and is of paramount importance.
Patch cables are interchangeable and backwards compatible. It is possible to plug a Cat5 cable into a newer model ethernet interface, but the data transfer speed will be affected. Likewise, a newer model Cat7 cable can be plugged into an old router and will work. In this case, there is considerable flexibility, but it is important to note that the speed may be impacted.
See the full RND patch cables overview with technical specifications, available colours and lengths here.
Optimising the workplace performance with RND cables
In summary the choice between ethernet versus Wi-Fi is a long-running one, but it will depend on your end user requirements of speed and security.
Whether you are building new network infrastructure in a commercial setting or upgrading existing cables getting the right one will help your workplace optimise performance.
At Distrelec, we offer a vast range of patch cables from many manufacturers, including our own brand RND which delivers great quality at competitive prices.











