With the growth of new technologies and advanced machines, the future of enterprises can be safer but also more prone to threats as everything is monitored and controlled online. Understanding what cybersecurity is today and how artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) can improve the safety of your facility is key to a well-functioning enterprise.
To illustrate how a better understanding of artificial intelligence and machine learning will assist both businesses and individuals in defending themselves against contemporary attacks, we will focus on highlighting solutions from industry leaders to guide readers in selecting the right cybersecurity solution with AI and ML implementations.
Common Cybersecurity terminology
Before coming to the substance of the matter, there are some common terms used in cybersecurity that will help you understand the concepts and later on discuss the solutions with IT professionals. You can skip this part if you already know the terminology.
Defence in Depth
The concept is built on many layers of security features that enhance the system’s overall security. In the event that one of the security measures is ineffective, the others serve as a backup to keep the network safe.
Industrial Firewall
To prevent unauthorised access, industrial firewalls are devices that monitor and block traffic to or from networks or network devices, such as industrial PCs, control systems, and other devices.
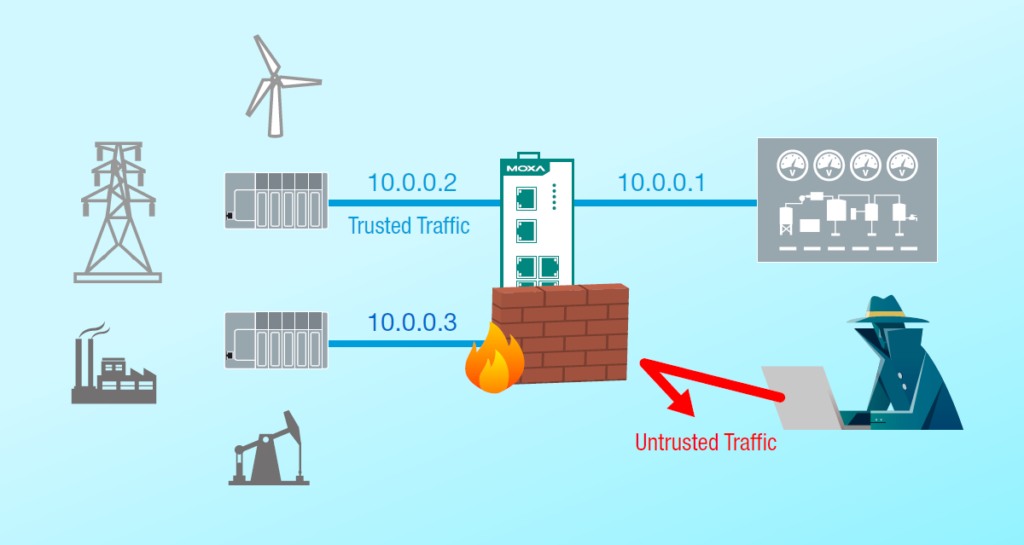
IDS (Intrusion Detection System)
An industrial IDS is a tool or system that monitors network traffic for any suspicious activity and sends out alerts. Any intrusive activity or violation is often recorded centrally using a security information and event management system, alerted to an administrator, or both.
IPS (Intrusion Prevention System)
An Industrial IPS is a tool or system that detects malicious activity, records details about it, reports it, and then makes an effort to block or stop it. It continually scans a network for harmful activity and responds to it when it does occur by reporting, blocking, or discarding it. It can be either hardware or software.
DPI (Deep Packet Inspection)
Deep packet inspection (DPI) is a sort of data processing that carefully examines the information being transmitted across a computer network and may take appropriate actions, such as alerting, blocking, re-routing, or logging in. Deep packet inspection is frequently used to monitor application behaviour, examine network traffic, diagnose network issues, make sure that data is in the right format, and look for, for example, malicious code, eavesdropping, internet censorship, etc.
Malware
It is a general term for any software-designed threats to cause damage to the computer, server, client, or computer network. Examples of malware are viruses, worms, trojans, spyware, rootkits, adware, remote access and ransomware.
DoS/DDoS
Denial-of-service (DoS) is an attack meant to shut down the machine or network, making it impossible to access for intended users. It can be done by delivering information that causes a crash or by flooding the target with traffic. To prevent the target from receiving or sending any information, distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks can be carried out by saturating the target with traffic from many hosts.
Why are Industrial Network Security and Cybersecurity important?
In the age of digitalisation, cybersecurity plays a key role in a properly functioning working environment. It protects all categories of data from sabotage, data loss or any other failures. With the growing technologies and more connectivity, monitoring and tracking potential cyber-attacks become more difficult, especially for analysts as they often need to fight back against AI.
Cyberattacks have cost companies money and criminal damage. Therefore, machines and devices are often designed to prevent and track the potential issues appearing on industrial networks. They can learn about and analyse potential cyber risks in real-time and increase cyber analyst effectiveness.

Artificial intelligence in cybersecurity – is it better than humans?
Analysing and enhancing cybersecurity is no longer a human-scale issue. AI and ML are more accurate and better than humans and traditional software at identifying patterns that indicate malicious software and unusual activity. AI and ML can analyse millions of events and quickly identify threats like viruses and zero-day vulnerability attacks.
As per Capgemini report, more than half of organisations (56%) claim that their cybersecurity analysts are overworked, and nearly a quarter (23%) are unable to thoroughly examine all incidents that have been reported.
Additionally, according to the report, 69% of enterprise executives will not be able to respond to cyberattacks without AI. 80% of telecom companies and 79% of customer goods producers say they depend on AI to help identify threats and stop attacks.
Applications of ML
Machine learning can be more efficient and better at detecting threats than human analysts.
As per Carbonite and Webroot, OpenText companies in their Fact or Fiction report based on a survey conducted between March and April 2021, more than half (57%) of respondents from around the world claimed that they were victims of a damaging cyberattack in the previous year [2020]. 65% of respondents from the report added that their organisations are more prepared to handle cybersecurity attacks because it uses AI/ML-driven cybersecurity tools.
Nowadays, even hackers use AI effectively. Artificial intelligence can send tweets way faster than humans, and it can respond more accurately as it fights other intelligent software. It only means that the implementations of ML and AI are not avoidable. They become a key weapon in fighting cyber attacks.
Therefore, companies are beginning to concentrate more on thwarting threats. The best applications will be in analysing enormous amounts of data and carrying out extensive operations to spot abnormalities, suspicious or unusual behaviour, and zero-day attacks.
Cybersecurity for Digital Enterprise – Siemens
Businesses and manufacturers are focusing now on many new implementations to improve their workplaces. From smart manufacturing, Industry 4.0 and 5.0 to Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) and Digital Twin. The industrial world is connected and monitored – that is what most companies strive for. However, as more things are moving to virtuality, new technologies are bringing different solutions to deal with cyber risks.
Siemens focuses on helping organisations fight cyber danger by sharing awareness on their website through study cases, whitepapers, as well as podcasts and videos (watch below). This brand knowledge and focus on important industry cases help create the best solutions to fight online threats.
Siemens Defence in Depth
Siemens has its own defence in depth and provides ways to fight cyber attacks. By following the international standard IEC 62443, Siemens focuses on a multilayer security concept that gives plants full protection, from plant management level to field and secure data communication.Click here to find out more about certifications and standards.
Plant security
Plant security is the protection and security management for automation systems. In order to prevent unauthorised individuals from physically accessing crucial components, plant security uses a variety of techniques, starting with standard building access and extending to the key card security of sensitive areas.
You can contact Industrial Security Services from Siemens that can help you with processes by providing guidelines for comprehensive plant protection.
Network security
In terms of network security, segmentation and encrypted communication are used to safeguard automation networks against illegal access. Remote access to equipment and facilities is becoming more common in the industry, and, as mentioned above, segmentation is providing additional security.
System integrity
System integrity means protecting automation systems and control components. Siemens provides integrated security features against unauthorised configuration changes at the control level and for unauthorised network access.
For example, SIMATIC S7 controllers and control systems like SIMATIC PCS 7 and PCS neo, SCADA and HMI systems can be secured against unauthorised access. System integrity comprises user authentication and access rights, as well as system hardening against attacks.
If you seek integrated security functions for protecting your investment and maintaining productivity levels, SIMATICs G120 Smart Access Module provides simple integration into the application and an easy set-up process.

The SINAMICs G120X operates stably under all network conditions, is extremely energy efficient, has various frame sizes and power ranges, and is used in a variety of industrial applications, from heating, ventilation, air conditioning systems, water to building and infrastructure, and more.
S7-1500 Controllers offer top-performance and reliable solutions for any machine and process control applications to build the digital factory of tomorrow.
Another device is this innovative touch screen SIMATIC HMI Comfort series that is able to coordinate its display via PROFI energy during break times and switch it off centrally to reduce energy consumption and maximum data security if power fails.
Other features:
- TFT widescreen display with high resolution
- Up to 1280 x 800 pixels are designed for the implementation of high-performance visualisation applications on the machine-level
- Precise diagnostics are made easy via different connection types: Ethernet, RS422, RS485, SD card slot
- USB 2.0 and integrated memory of 24 MB
- More interfaces and fewer hardware costs for efficient operator control and monitoring

Secure your Industrial Networks – MOXA
Moxa’s commitment is to ensure reliable connectivity for industrial environments. As many industrial networks are exposed to cyber threats, Moxa has developed an enhanced network security portfolio. The brand provides Industrial Cybersecurity Solutions that include critical IT cybersecurity technologies, such as an Intrusion Prevention System (IPS), a key component for defence-in-depth strategies.
Their industrial cybersecurity solution has been specifically designed to protect industrial networks from cyber threats without disruption to industrial operations. Similarly to the other brands highlighted within this article, cybersecurity is a core focus for Moxa. They provide many supporting sources to help you understand the cyber risk better and find the best solutions for any malware.
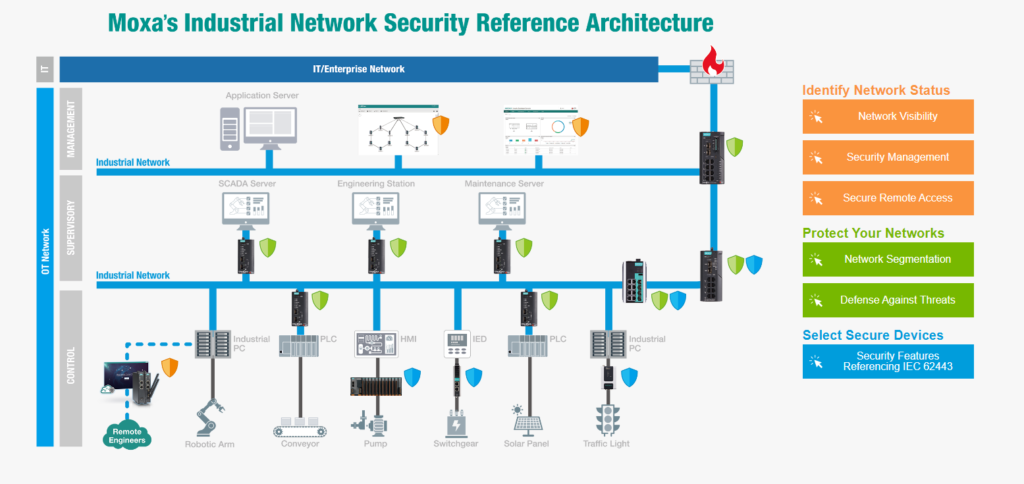
Moxa Secure Connections
There are more and more cyberattacks targeting industrial networks, and it is crucial to identify and mitigate vulnerabilities before they can be exploited. Companies need to make sure that the network architecture supporting their industrial networks is secure, allowing only approved traffic to pass through to the right locations.
Getting reliable and secure data transfer from operational technology (OT) devices to IT-based cloud services is a major difficulty for many system integrators and engineers in the IIoT. The combination of Moxa’s strong, cloud-ready IIoT gateways and value-added, long-lifecycle software offers secure and dependable IIoT solutions that can be quickly built and implemented in the field. Moxa provides OT/IT integrated network security solutions by fighting cyber threats in two ways:
- Reinforce your network infrastructure using device-by-device and layer-by-layer security capabilities to ensure legitimate data traffic on the network remains safe.
- Protect your critical assets and networks with specific OT protocols and packet inspection, as well as pattern-based protection.
Moxa enables secure edge connectivity as it is really important to ensure that devices on the edge are securely connected, before applying another layer of protection (segmenting the network with routers and then securing assets with IDS/IPS/Firewalls). Moxa’s multilayered cybersecurity approach is based on the industry standard IEC-62443 and the brand secures your OT networks with OT/IT Integrated security by:
- Uniting Networking and Cybersecurity – combines industrial networking and cybersecurity expertise to provide layered protection for your industrial network.
- Continuously Enhancing Security – Moxa takes a proactive approach to protect our products from security vulnerabilities and help users with better security risk management.
- Developing IT/OT Security – Moxa is a TXOne Networks partner that responds to the growing security needs of industries as well as the security demands of IT/OT personnel.
The brand’s offering include centralised network and security management and remote connection management, protection of industrial assets with IPS and IDS secure network and edge connectivity with hardened industrial networking devices.
From Distrelec you can get a wide range of edge connectivity devices such as protocol converters and serial to ethernet device servers from Nports 6000 (see below) to Mgate MB3000 series. Ethernet and wireless connectivity might be delivered by some managed switches, including smart managed SDS-3008 and a new Wi-Fi products AWK-series coming soon in Q1 2023 (IEC 62334-4-2 certified).
Serial Device Servers
The NPort 6000 device servers use the SSL and SSH protocols to transmit encrypted serial data over Ethernet. The SSL and SSH protocols, which function by encrypting data before transferring it over the network, are supported by the NPort 6000 in order to address this issue. Users may be certain that serial data is sent securely across both private and public networks with the NPort 6000.
Other features:
- Secure operating modes for Real COM, TCP server, TCP client, paired connection, terminal and reverse terminal
- All baud rates are supported with high precision
- Network medium selection: 10/100BaseTX or 100BaseFX
- Automatic RS-485 data direction control with patented Moxa ADDC
- Port buffer to store serial data if the Ethernet is not available
- SD slot to expand the port buffer memory
- Extended operating temperature range: -40…+75°C

Find out more on how Moxa helps secure your industrial networks in Europe here.
Getting started with Industrial Cybersecurity – Hirschmann
As mentioned above, digitalisation and the growing interconnection of machines and industrial systems obviously improves the facility but also can expose the company to cyber risk. According to the brand’s source, attacks on manufacturing plants increased worldwide. Therefore, the protection of industrial facilities is crucial against internal and external thwarts.
Hirschmann, a Belden’s brand, is committed to providing industrial cybersecurity solutions. The brand focuses on high-end industrial networking solutions. Among the wide range of products are industrial connectors, controlled and unmanaged Ethernet switches, media converters, wireless LAN, and security.
A few ways to start with industrial cybersecurity:
- Network Assessment – look at your OT network to find out all devices connected to it, such as machines, sensors, controllers, drives, switches, cameras, etc. Then, you can determine how the devices are being used and establish a baseline to monitor and measure each device over time to track changes.
- Identify any cyber attacks – scan and identify IP addresses to discover new unknown devices without creating additional traffic or latency. This can assist in identifying rogue or illegal devices that are exchanging data during the discovery phase. You can then conduct further research to learn more about such devices and assess their potential for damage.
- Develop a defence-in-depth strategy – it is basically an approach to cybersecurity from planning how to protect valuable data and prevent everything downstream. The strategy allows for identifying the bare minimum required between moving from one device to another, for example, after collaborating with plant managers in charge of SCADA networks to determine what information must flow from a cell of robots out to various industrial equipment via PLCs and HMIs.
- Segment your network – network segmentation can help improve security. For example, separating OT networks from other networks internally and externally allows for securely shared data. Separating/ segmenting the network might help to not ‘spread’ the threat to other devices (if the attack happens on one segment of the network, the other segment will not be impacted).
Once you know a little bit, you can start improving your cybersecurity strategy (defence in depth).
Hirschmann offers end-to-end cybersecurity solutions, from firewall solutions to routers and network software. Watch the video below to find out more about industrial firewall EAGLE40 features.
Industrial Cyber Security – Phoenix Contact
Phoenix Contact is another Distrelec supplier that provides solutions for basically every industry, from machine manufacturers, system operators, and the automotive industry to energy, water and oil and gas industries. The brand can help you with achieving the maximum possible stability and transparency for your infrastructure by selecting the appropriate and necessary hardware.
There are plenty of solutions to cyber risks, and Phoenix Contact showed typical examples of threats and how to solve them.
| Risk | Solution |
| Multifunctions from the office | Network segmentation |
| Hacker attacks | Encrypted data transmission |
| Malware attack | Restricting communication |
| Infected hardware | Protect ports |
| Unauthorised access to systems | Secure remote access |
| Inadequate user management | Central user management |
| Mobile end devices | Secure WLAN password assignment |
| Unsecure or incorrect device configuration | Device and patch management |
In the brand offer, there are products with security functions, such as secure user authentications, network segmentation, network monitoring and firewall functions or the use of secure and encrypted communication protocols.
Phoenix Contact automation solutions
In compliance with international standard IEC 62443-2-4, Phoenix Contact has the capacity to create and launch secure automation systems. In accordance with a protection requirements analysis and the protection goals of confidentiality, integrity, and availability, the company provides secure automation solutions. Threat and security risk analyses are also included in their services.
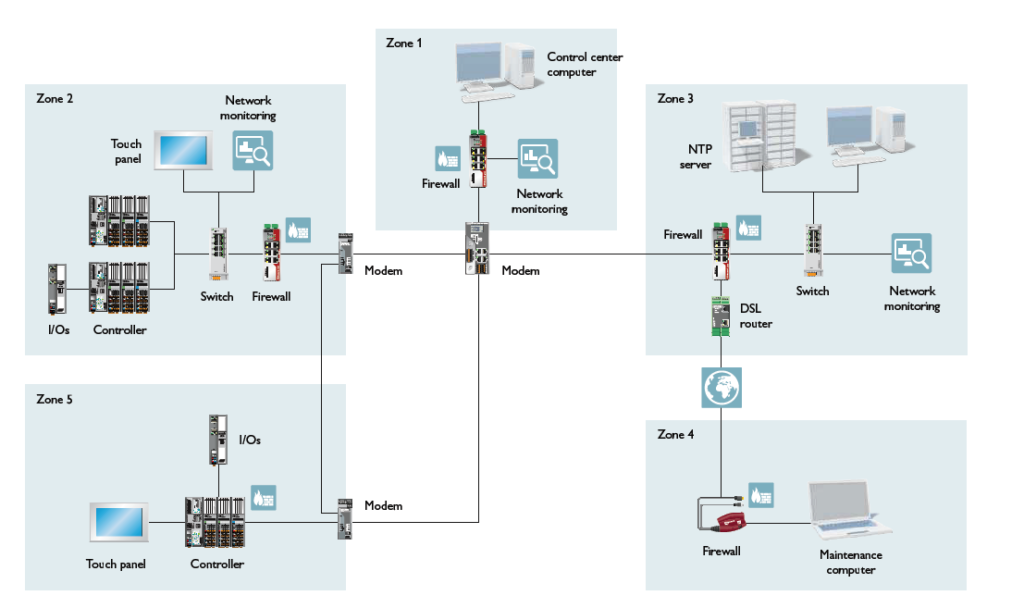
Similar to other brands mentioned earlier, Phoenix Contact provides services from evaluation and planning to implementation, maintenance, support and even seminars. Below you can find some of the products that provide security from development to patch management.
mGuard Security
The core of your system consists of mGuard security routers. Deep packet inspection for industrial protocols, conditional firewalls, user firewalls, and secure network access for service professionals are just a few of the unique firewall features they provide. Additionally, you have access to a system for quick, secure remote maintenance through the mGuard Secure Cloud.

PLCnext Security
The PLCnext Control devices are, as the brand claims, ‘secure by design’ in accordance with IEC 62443 certification. They are scalable controllers with an IP20 level of protection. With solutions for any IOT application, PLCnext logic controllers build an ecosystem for endless automation. Benefit from PLCnext is a highly adaptable open control platform, modular engineering tools, PLCnext store, cloud integration, and community sharing system.

Phoenix Contact products are subject to vulnerability management (PSIRT) where security patches and updates are provided for any security vulnerabilities that are identified.
Conclusion
The cyber risk will grow, and companies need to be prepared that there can be more online threats attacking their systems in the future. Some of the solutions presented above can help you secure your networks. With a proper defence in depth, industrial firewalls and IPS or IDS, you have a high chance that the untrusted traffic will be stopped. Today, to fight against systems, you need to implement similar tools that can quickly predict and adapt to online risk situations. It often has to be ML or AI fighting against another machine or advanced expert system.











