The clean environment is one of the most important things that society strives for. Countries and within them corporations are setting targets to achieve net-zero. But how to create sustainable manufacturing if industries are one of the most significant global greenhouse gas emissions sources? Many companies will need to transform their industrial system to minimise environmental impact.
Sustainable manufacturing
Manufacturers must strive for new and inventive methods to achieve flexible, resource-saving manufacturing, which will ultimately contribute to the vision of an autonomous factory. Every stage can be more manageable and environmentally sustainable with automation. But to create more sustainable production, manufacturers and factory owners need to redesign their workplaces. To make sure your company is growing, you have to look at:
- Sourcing: it is crucial to source sustainable, raw, and recyclable materials for your products.
- Producing: while producing your components, it is essential to increase operating efficiency, eliminate waste in the manufacturing process, apply smart manufacturing technology and utilise renewable energy sources.
- Delivering: delivering products requires establishing carbon targets for transportation providers and collaborating with them closely. It will lower the carbon footprint of shipping raw materials, components, and finished goods.
- Service: by providing replacement parts, repair and disposal services anytime for your customers, as well as improving the recycling and efficiency of products in the field, you and your company are moving toward a circular economy model.
How does automation improve sustainability?
Sustainability will be one of the top trends in industrial manufacturing in 2022. The tendency towards more ecological industries is growing. Earlier companies were putting changes in response to stakeholder demands, environmental concerns, regulatory regulations or direct financial benefit. Now, change is a necessity.
Emissions will have to be reduced by even greater amounts to hit net zero by 2050.
The Guardian, ‘Reality check’: Global CO2 emissions shooting back to record levels
Renewable energy and waste reduction
Today’s leading industrial producers face many challenges to ensure energy efficiency. Do you know how to produce energy at a lower cost-effectively? How to reduce overall energy consumption that contributes to considerable reductions in greenhouse gas emissions? Manufacturers with vast enterprises invest in on-site generating, such as solar panels, wind turbines, and geothermal pumps. But depending on the size of your business, you can start with small steps towards a sustainable economy.
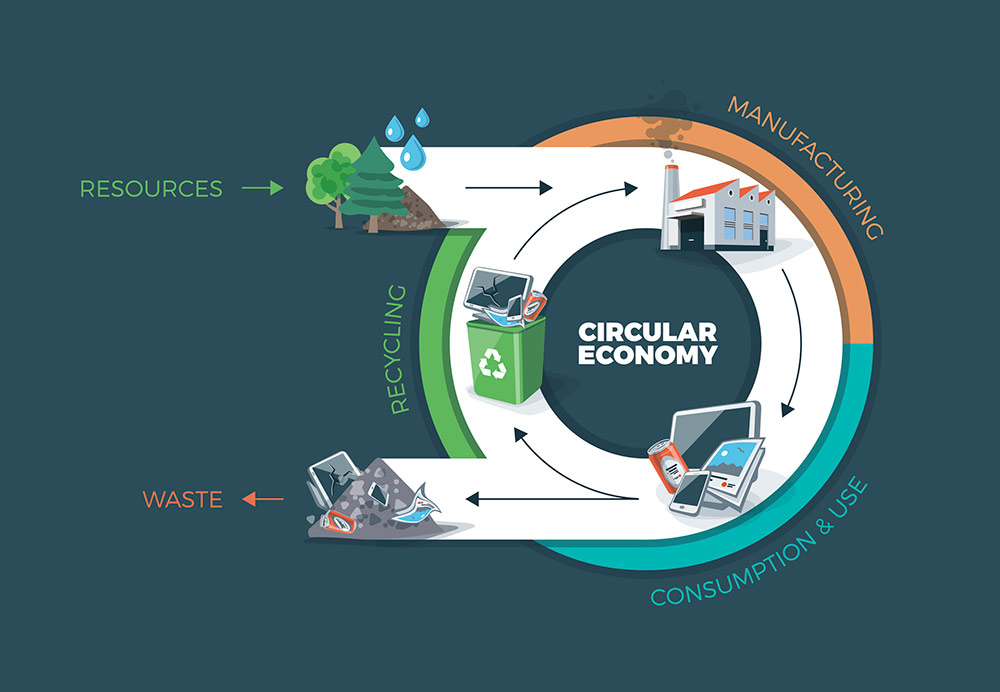
Manufacturers can address their single biggest sustainability challenge while reducing environmental impact and conserving resources by incorporating sustainable practices into their processes. It can lower costs by reducing waste and water consumption, changing energy loads, and tapping into renewable resources.
Digital technology can significantly help with this. Automation in manufacturing allows workers to observe the energy usage and have it under control. As a result, organisations can increase predictive maintenance to reduce energy loads, material and water waste.
Renewables could grow to around 27% of total final energy consumption for global manufacturing by 2030, assuming the availability of low-cost, and sustainable, biomass sources as well as reduced capital costs for emerging technologies, and potentially around 34% if carbon-emissions pricing is widely implemented.
International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA)
Digitalisation and new technologies
The rapid pace of digital transformation opened up new horizons for companies to build more sustainable industries. However, the way to digitalisation was not without obstacles. According to the World Economic Forum, the Covid-19 pandemic has compounded problems with basic hygiene, pollution, exploitation and abuses, making it difficult for countries to establish more balanced economies. It was also a test for many businesses to start using new technologies in their workplaces. Thus a lot benefited from the transition to the new way of working.

Technologies such as cloud computing, predictive analytics and machine learning enable energy and utility companies to establish a digital customer model. In agriculture, technology assists farmers in automating decision-making by analysing soil, weather, and labour variability, among other factors, as well as in automotive industries to provide usage-based insurance.
Human-machine interfaces allow people to develop their creative capacities and productivity, while robots handle repetitive roles without human interventions. Especially in the environment, smart technologies including AI, IoT, blockchain, ML and digital twin help reduce air pollution, enable resilient operations, and improve people’s lives.
Autonomous production
The future of manufacturing is autonomous and automated. It means factories have to focus on innovation and optimisation of production techniques and processes. Adapting modular, cell-based manufacturing systems help with the shift to more linked, autonomous logistics and material flow in plants.
Implementing 3D print, IoT, and automatisation add efficiency and lower production and labour costs. Manufacture can be placed in flexible, distinct cells rather than sequentially on the production line. Besides that, gathering data from various production cells and performing the smart analysis can be relayed back to line operators to optimise assembly line maintenance.
As per Siemens, the traditional overarching, planned-out procedures will give way to flexible, modular manufacturing. Smart transport and handling technologies will lead in this new production strategy, and the best path will be imagined, simulated, and executed in real-time. Siemens already uses automation in control cabinet manufacture, a mix of digital twins and AI-based systems. Read more about the evolution of the industrial control cabinets in the IIoT era.
How can your company make the shift to sustainability?
The change towards a sustainable economy can’t happen in one day. Manufacturers should start by introducing small technologies in some parts of their factories. Then focus on developing smart technologies, such as IT, data and communication infrastructure.
Energy transition and digital transformation are rapidly changing what work we do, how we do it and where we do it. However, growing competition for both sustainability and digital competencies [from other sectors], an ageing workforce, fewer new recruits and a lack of diversity all point to increasing skills challenges in the future.
Deloitte
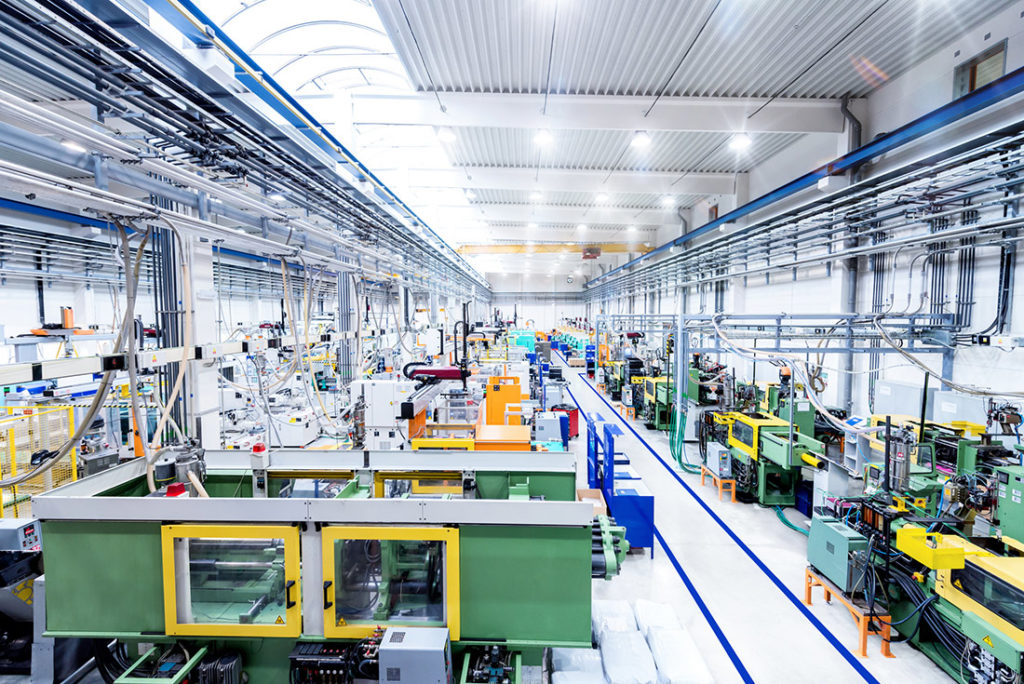

Autonomous factories have the potential to have sustainable results and save costs. But to be ready for the changes, it is essential to take a few points into account:
- Check the current carbon profile of your facility.
- Plan a strategy focused on decarbonisation.
- If the carbon footprint is under control, focus on implementing automation in your manufacturing.
- Expect companies’ data to be audited to provide proof to clients of their levels of sustainability.
Besides the factory floor plan, there have to be some changes concerning staff:
- Build the net-zero workforce.
- Implement new roles.
- Collaborate with ecosystem partners, including suppliers, energy providers, industry groups and regulators.
Summary
Investment in modern sustainable manufacture can improve the environment and your business. However, it has to be done with a plan focusing on technologies and automation. Start from a decarbonisation strategy and implement new, innovative technologies focused on automating the industry. Thinking about technology and more ethically about materials sourcing, investing in the planet by waste reduction and reducing air pollution create a better environment. Furthermore, choosing suitable suppliers and partners can help achieve progress towards a sustainable economy.
Recommended products
HMI Programmable Terminal 12.1″ 800 x 600 IP65, Omron Industrial Automation
The NS-series HMIs offer the highest level of compatibility with the tried-and-true CS/CJ-series controllers, allowing for even more added value in user machines. The NJ-series Machine Automation Controllers can be used to build a flexible, high-speed, high-precision system. To make the most of the strengths of the NJ-series Controllers and to manage machines, use tags to access any memory locations or troubleshoot machines and systems using the NS-series HMIs.

Programmable Logic Controller 14DI 10DO 28.8V, Omron Industrial Automation
It is compact in size but it packs a punch in terms of capability. The NX1P machine controller completes the NX/NJ machine controller family, providing the same capability in a smaller design. Under one Integrated Development Environment, the NX1P provides synchronised control of all machine devices such as motion, I/O, safety, and vision.

Industrial Computers, RevPi, Kunbus
This Industrial Computers from Kunbus allows industrial sensor data to be transferred to the cloud via an Edge gateway. The PiBridge system bus can be used to connect all RevPi IO and RevPi Gate modules. The ConBridge system bus may connect a variety of transceiver modules. Some of their features: Quad-core ARM Cortex A53 1.2 GHz processor, 1 GB RAM, 4 GB Flash storage, 1 digital input and 1 digital output.

Microcontroller Boards, Arduino Portenta
Products from the Portenta family are designed for a variety of industrial and use cases while maintaining Arduino openness and being ready for the most demanding professional applications. Arduino has used its expertise in making high-quality PCBs in-house to ensure that their products can withstand the vibrations and temperatures encountered in everyday industrial, automotive, and agricultural applications.

Communication Module for ET 200SP, RS-422/RS-485/RS-232, Siemens
SIMATIC ET 200SP CM PTP communication module for serial connection is simple to use and compact in size. Safety integrated with hot swapping and communication with PROFINET AND PROFIBUS. It has a TIA Selection tool enabling reliable diagnostics. Features: RS-422, RS-485 and RS-232, freeport, 3964 (R), USS, MODBUS RTU master, slave, max. 250 Kbit/s, suitable for BU type A0, pack quantity: 1 unit.

MODBUS Communications Module LOGO, Siemens
LOGO CIM communication interface module has 8 ModbusRTU (RS232/485) interfaces Web configuration and 4-port Industrial Ethernet switch, no 4G/LTE engine; no antennae. This module is GPS integrated.

RISC Linux Embedded DIN-Rail Computers, UC-5100, Moxa
The UC-5100 Series embedded computers are designed for industrial automation. In a compact, front-end access enclosure, the computers have 4 RS-232/422/485 full signal serial ports with adjustable pull-up/pull-down resistors. The UC-5100 Series computing platform includes variants with two CAN ports and a small PCIe slot for wireless connectivity, as well as a dual-SIM architecture for network redundancy, to meet the needs of various industrial applications. The vertical DIN-rail form factor of the UC5100 makes it simple to fit the computer into a tiny cabinet. This space-saving method also makes wiring simple. As a result, the UC-5100 is an excellent choice for front-end embedded controllers in industrial applications.

Multifunction Energy Meters, Siemens
The Power Meter Sentron and Power Monitoring Device offer reliable recording of all consumption data for electrical branches or individual consumers. Thanks to a large functional and performance spectrum, they offer a wide range of applications. Both are compact in design and have a clearly legible display, even under poor lighting conditions. You can connect them easily to higher-level automation and power management systems.












