Healthcare has always been inherently human – from how we’re cared for to its fundamental battle with mortality – but it is now increasingly embracing the presence of machines. Surgical robots and advanced technology are the main drivers of this transformation.
Artificial intelligence (AI) and robotic technology are key in the healthcare sector by reimagining how health professionals work, as well as the ways in which patients are diagnosed, treated and cared for.
From surgery to general practice to research, every aspect of healthcare is being transformed. Here are seven robotic and AI applications set to make an impact, today and tomorrow.
1. Surgery
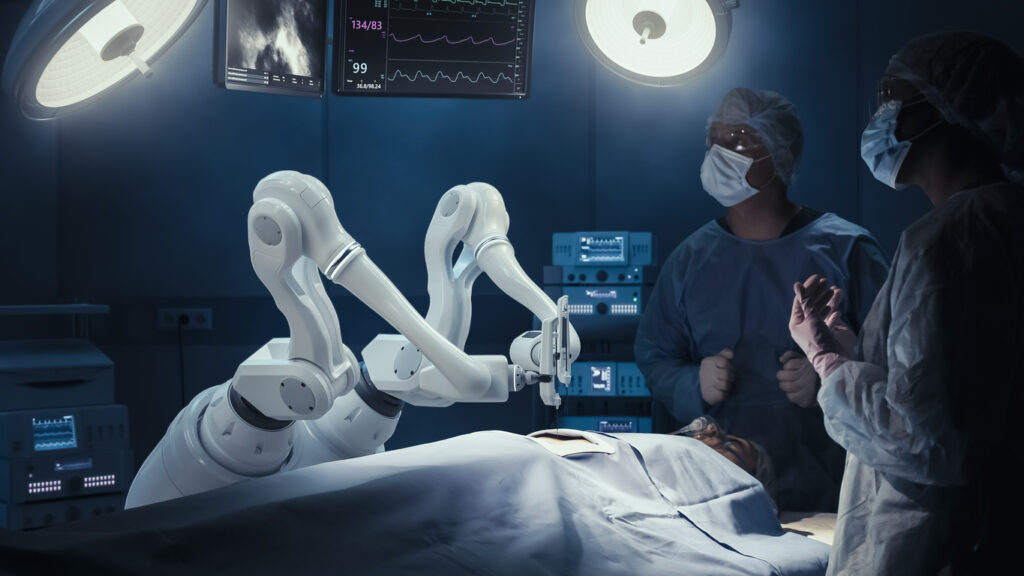
Da Vinci Robotic Surgical System
The da Vinci Surgical System is the most widely used surgical robot. Created by Intuitive Surgical, the da Vinci robot is utilised for several surgeries in hospitals and medical facilities across the globe.
Da Vinci Robotic Surgical system is renowned for its accuracy, control, and capacity to enable minimally invasive operations, which save patients’ recovery periods and reduce scarring. Its popularity is due to its broad adoption, the multitude of treatments it can execute, its proven track record, and ongoing technological developments.
The first da Vinci system was released into the market in 2000 after being approved by the FDA (The US Food and Drug Administration). To improve its features and capabilities, it has undergone multiple updates and changes since then, keeping up its status as a top instrument for robotically assisted surgery.
2. Dentistry
Yomi
Yomi is a robotically assisted dental surgery system designed by Neocis to automate and assist dental implant procedures.
Yomi, which consists of a single dexterous arm, is designed to operate in tandem with the dentist by monitoring the patient and guiding the drill to guarantee proper placement, depth, and position. Its software can be used to pre-plan a procedure based on a patient’s CAT scan and allows for quick changes.
Yomi is a significant advancement in dental surgery, especially with regard to implant operations. It was granted FDA clearance in 2016.
3. Nursing
Autonomous robot TUG
Designed by Aethon to assist logistics in hospitals and healthcare facilities, TUG is an automated robot system that delivers food, drugs and other clinical supplies.
TUG is a remotely operated, self-loading mobile cart with built-in maps and Lidar sensors for 360-degree 3D vision—the same technology used in self-driving automobiles. It is powered by intelligent software algorithms. This enables it to move along hallways and into lifts, as well as around patients and staff.
By efficiently performing mandatory tasks 24/7 with fewer mistakes, TUG and other medical robots are lowering costs and enabling nurses to spend more time caring for patients. Moxa is one of the brands that provides interconnected devices for medical applications, such as e-nursing carts, automated analysers, pharmaceutical packaging, and other smart medical devices. Find out more here.
4. Rehabilitation
Cyborg HAL
The HAL (Hybrid Assistive Limb) from Cyberdyne is a cutting-edge exoskeleton suit that helps users enhance and increase their physical skills. As a major advancement in medical and assistive technology, HAL is among the most sophisticated robotic rehabilitation devices.
By sensing bioelectric signals from the wearer’s muscles to aid with movement, it improves physical capabilities. It helps people with ailments including strokes and spinal cord injuries move more freely and is frequently used in rehabilitation.
HAL is a significant advancement in wearable robotics and rehabilitation technology. It is still evolving, with multiple variants for varied applications.
5. General practice

Babylon
AI improves healthcare by lowering workloads for physicians and boosting diagnostic accuracy, freeing them up to focus on patient care and patient experiences. One example is Babylon (now eMed), an AI-powered smartphone app, providing individualised health assessments, virtual consultations, and symptom checks. It offers medical diagnosis alongside 24/7 video access to real doctors and e-prescriptions.
Prior to asking the patient to map pain and its intensity on a human body using a touch screen, the chatbot goes over the patient’s symptoms with them. To arrive at a diagnosis, it then examines the patient’s medical records in addition to more than 300 million data points from research publications and other patients.
Utilising AI-powered chatbots and virtual health assistants to arrange appointments, communicate with patients, and deliver information is one of the most recent developments in virtual assistant technology, and it is the future of healthcare. Even during the COVID-19 pandemic, remote monitoring and AI became essential for maintaining patient-doctor connections. We can expect these technologies to grow in the coming years.
5. Research

AI-equipped microscope
This AI-powered microscope designed by Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Centre (BIDMC) is being developed for use in hospital laboratories to diagnose deadly blood diseases.
A convolutional neural network (CNN) is a type of artificial intelligence that is utilised in microscopes to interpret visual input. It is modelled after the human visual cortex. It can identify and group bacteria according to their morphology and distribution using machine learning.
The proficiency required to reliably and precisely identify microorganisms will decrease, and procedures and diagnosis times will be accelerated, allowing patients to receive vital care more quickly.
The idea is to combine the skills of a microbiology technologist and AI. Specifically, an automated microscope will capture hundreds of images from the patient specimen. The AI program would then identify select images containing microbes and present them to a technologist on a computer screen with a proposed diagnosis. The technologist would then scan the on-screen images and confirm the diagnosis. Microbes are often very rare in specimens, and it may take a long time for a technologist to identify microbes through the standard manual way. Technologist assistance would reduce the technologist time needed for a diagnosis to seconds.
Dr James Kirby via Digital Trends
7. Prevention
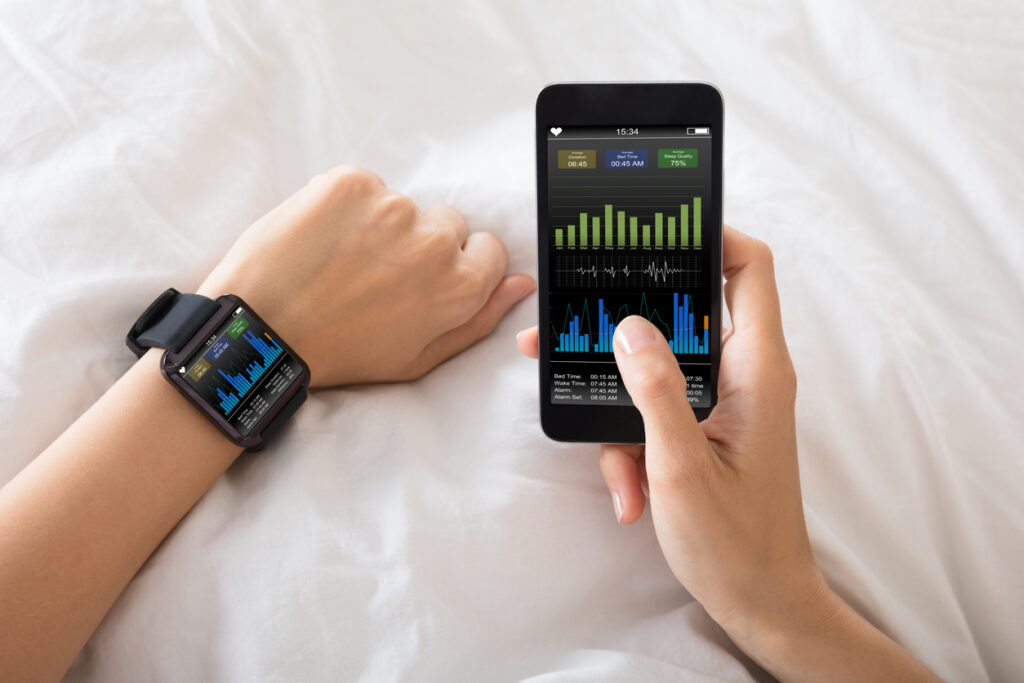

Smartwatch
Currently, a lot of popular companies, like Apple, Samsung or Garmin provide smartwatches able to recognise and keep track of a variety of medical conditions. They often have a mix of sophisticated fitness and health tracking functions.
For instance, the Apple Watch can measure blood oxygen levels, detect falls, conduct ECGs, identify heart rate anomalies suggestive of atrial fibrillation, and even provide handwashing detection. Whereas Fitbit Sense is well-known for its stress management tools, heart rate tracking, and skin temperature monitoring capabilities. It also has a sleep tracking feature, an ECG app, and an irregular heartbeat notification feature.
Smartwatches are being utilised more and more as devices for proactive health monitoring, providing users with early alerts and insights about possible health problems in addition to measuring fitness. Nonetheless, for medical advice and diagnosis, it’s crucial to always speak with healthcare specialists. These are mainly gadgets that are meant to be used in conjunction with professional medical care, not as a substitute. Find out how advanced wearables have developed over the last few years.
AI and robotics are transforming healthcare – not by replacing the human face of care, but by assisting it. Doctors, nurses, and other medical workers may provide better, faster, more accessible services, enhancing treatment and saving lives.
Advancements in diagnostics, imaging and treatment have been driven by AI with algorithms to improve the interpretation of data, such as X-rays and MRIs as well as predicting outcomes and diseases. From robotics in hospitals to remote teletech services and the use of chatbots, AI is impacting the healthcare industry in a number of ways.











