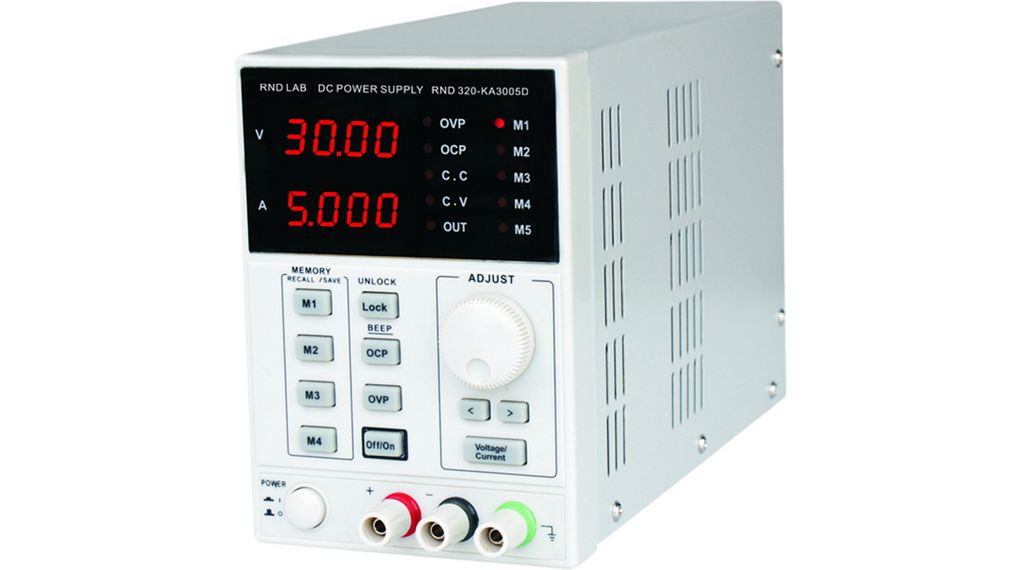
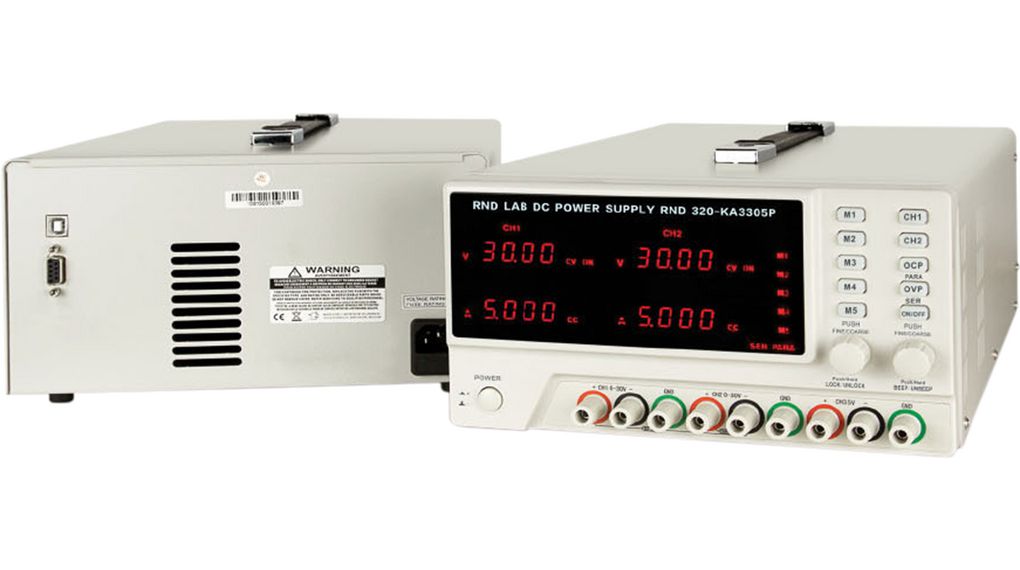
Bench top power supplies or ‘laboratory power supplies’ are a fundamental component of any test and measurement setup. Bench top power supplies are an essential piece of equipment for electrical and electronic testing. They are very commonly used tools by engineers and circuit architects to power, test and measure circuit designs. They provide a variable and reliable voltage supply, ideal for a range of applications anad projects.
Variable DC bench power supplies have an additional safety feature in the form of being able to set a maximum current value. This enables the power supply to cut the electricity supply if a short circuit has been detected. RND Bench Top Power supplies are the ideal option to safely power your projects at an affordable price because they come with built-in overvoltage and overcurrent safety.
Features of bench power supply
Bench power supplies convert mains alternating current (AC) and provides a direct current (DC) output to power small electronic devices and circuits at a range of different voltage levels. Their primary function is to provide power to electronic devices under test (DUT) to inspect if they work as intended.
Bench power supplies are a dependable and reliable source of power that do not interfere with the operation of the circuits that they power, letting the user concentrate on design and diagnostics. They also have far greater current and voltage control than ordinary AC-DC wall bugs and converters, meaning they enable precise control over the controlled DC.
They owe the name ‘bench power supplies’ or ‘benchtop power supplies’ to the placement as they often sit on an engineer’s work area or bench.
Features of RND Bench top power supplies:
- Finely adjustable current and voltage settings
- Low noise and ripple
- 10 mV / 1mA resolution
- Programmable and adjustable output options
- Keyboard lock functionality
- Power-off memory function
- Output options of 1/3/4

The most common applications:
- Electronic Design Laboratory
- Research
- Production and manufacturing
- Workshop
- Education
Types of bench power supplies
The three primary types of benchtop power supply are linear/switching, single/multichannel, and bipolar/unipolar. Although they exist in a wide variety of configurations, these three main categories are the most popular.
Linear and Switch-mode power supplies
A linear power supply can provide high-accuracy measurements with extremely little noise and signal interference. They are, however, often heavier, bulkier in size, and produce less power at a reduced efficiency. Switching power supplies, on the other hand, are more compact and can provide higher levels of power, but they suffer from high-frequency noise and have less accurate readings. When high power with a low footprint is needed, a switching power supply is the power supply of choice since it can deliver substantially more watts with a smaller footprint. A linear power supply comes into its own when being used to power applications with delicate analogue circuitry.
Single and multi-channel power supplies
As the name implies, a single-channel bench power supply unit has one controlled output. Multichannel, on the other hand, has two or more output possibilities. The one-controlled output in a single-channel power supply makes it less versatile and less expensive. In contrast, multiple adjustable outputs are ideally suited for analogue and digital circuitry use while working on devices that require varying voltage inputs.
Bipolar and Unipolar power supplies
A unipolar power source can only provide positive voltage. A technician can manually flip the terminals attached to the power source to produce a negative voltage, however this is often very inconvenient. Bipolar power supplies, on the other hand, can produce both positive and negative voltages. As a result, they can handle a greater range of practical applications, such as the creation of magnetic materials for car motors, bidirectional inverter testing, and laser diode testing. They are, however, a lot more expensive and complicated than a unipolar power supply.
How to choose the correct bench power supply
There are some important factors to consider before purchasing a power supply. These include the required voltage & current range, number of outputs, and voltage/current limiting.
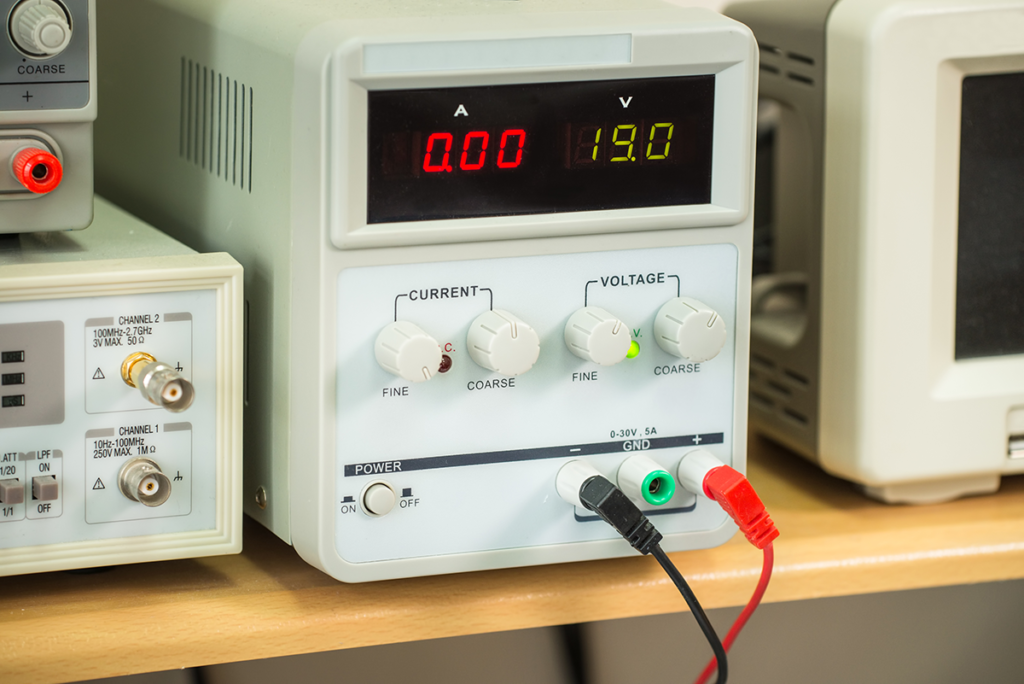

Setting current and voltage
Setting voltage levels and current restrictions might be time-consuming when doing long or complex tests. A bench power supply does, however, have two very useful modes of operation: constant voltage and constant current. Fortunately, most bench power supplies have a test sequence capability that provides a basic amount of programmability.
It is possible to programme voltage values, current limit values, and duration per step using the test sequences function. This is a simple method for executing a complex test with various predefined output voltages and timings without having to manually change the settings on a power supply.
Setting the current limit is important because too much current will destroy a circuit. Simply anticlockwise crank the voltage and current knobs. The monitor will indicate cc, which stands for continuous current. Connect the output leads. Unclip the leads after turning the current knob clockwise to the desired level.
On the other hand, setting the voltage is easier. Simply turn the voltage knob clockwise to the necessary level. The power supply is now ready for use.
In a typical supply, a multimeter can be used to measure the output voltage at regular intervals. A built-in display on a programmable power supply shows all of the important information, such as current voltage, set current, mode of operation, and many other factors. You can purchase True RMS Autoranging Digital Multimeter from RND. Find out more here.
Other important things to consider before buying new benchtop power supply:
Number of outputs
Multiple output power supplies with high accuracy have grown more economical, it is important to consider how many outputs will be required in general use. Although single output power supplies are adequate for many applications, multiple-output power supplies can often provide many significant benefits. Two or more outputs would be preferable for more complex requirements.
Noise
Spurious AC components on the output of a DC supply are known as ripple and noise, or periodic and random deviation (PARD). The word ‘ripple’ refers to the small unwanted residual periodic variation of the direct current (DC) output of a power supply which has been derived from an alternating current (AC) source. Noise is classified as the random high voltage spikes that occur on the output. Choose a power supply that produces little noise and ripple, resulting in greater clarity in the workplace.
Response time
When testing with rapidly changing voltages, response time is critical. The response time of a device is the time it takes to increase or decrease a specific voltage. This fluctuates according to the load. Choose a supply system that is appropriate for the purpose.
Overheating protection
Overheating might cause the power supply to shut down, and potentially cause damage to the device. Select a device with overheating protection. This will ensure a long service life.
Programming
Consider choosing a bench power supply with a test sequence feature rather than wasting time manually setting voltage and current limits. Users can employ pre-programmed settings with a fully programmable power supply. This feature saves technicians vast amounts of time having to manually configuring the test sequence for each test.
Remote sense voltage monitoring
If you are running tests with rapidly changing voltages or loads, To acquire the most precise voltage supply, use a power source with a remote sensor. By correcting voltage loss from the test terminals, remote sense voltage monitoring receives measurements at the Device Under Test rather than at its input ports. This results in a much cleaner reading.
Shutdown memory
To save valuable measurements and configurations, select a machine with built-in shutdown memory. This ensures that all of your data is safely preserved in the event of a power cut.
Finding the best bench top power supply
A well-designed, feature-rich laboratory power supply provides both superior performance and the additional capabilities and functions required for efficient and flexible use, such as convenient front panel control, networked access, and script-driven programmability. You can find some of such power supplies in the Distrelec webshop, available from the RND brand. RND offers power supplies for operation with constant voltage and constant current with fully digitised control, overload protection and compact solid metal housing, as well as a large LED display.
Have a look below and choose the best benchtop power supply from RND!
Recommended products















