Healthcare is a crucial industry that helps treat many diseases, including rare ones. Significant advancements in technical innovation in the field of medicine have been crucial in enabling breakthroughs in treatment and care as well as a deeper understanding of human health.
The latest medical technology greatly advances our knowledge of the human body, but progress towards a healthy future depends on addressing issues like growing healthcare costs, rising inequalities, and climate change, therefore, some of the newest healthcare industry trends are expected to help address these challenges.
Table of Contents
- Latest Emerging Technologies in Healthcare in 2024
- 1. Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare
- 2. Integrating Data and Predictive Analysis
- 3. Nanomedicine
- 4. Augmented & Virtual Reality in Healthcare
- 5.Technology in Mental Health
- 6. Remote Patient Monitoring & Virtual Care
- 7. Digital Twins for Health
- 8. Wearables in Healthcare
- 9. Organ Care Technology & Bioprinting
- 10. Healthcare Data Management
- Future Healthcare Technology Trends
Latest Emerging Technologies in Healthcare in 2024
The technology used in healthcare creates new opportunities for patients and medical personnel to live in a more sustainable environment and fight even previously incurable illnesses. The presence of technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI), machine learning, virtual care and the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) strongly improve medical facilities. Read on to discover new healthcare technology trends.
1. Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare
Artificial intelligence is developing across many industries, among others, healthcare. With several applications, such as examining patient information and other data, and the ability to develop new medications and improve the effectiveness of diagnostic procedures, healthcare and AI are dramatically changing the industry.
Machine learning, which is a type of AI, has a huge impact on the healthcare sector. Machine learning healthcare technology was helping, for example, to analyse CT scans in order to treat the effects of COVID-19. But there are several other uses for artificial intelligence that go beyond pandemic treatment. For example, AI improves cancer diagnostics. For decades, the main way to diagnose cancer disease was biopsy, but it did not provide the full picture of the organ tissue. Now digital scans of a particular region that cell mutations may impact are a key component of contemporary histopathology techniques. Pathologists can look at considerably bigger portions of the human body at once using entire slide pictures or WSI (whole-slide imaging).
The promise of artificial intelligence in medicine is to provide composite, panoramic views of individuals’ medical data; to improve decision making; to avoid errors such as misdiagnosis and unnecessary procedures; to help in the ordering and interpretation of appropriate tests; and to recommend treatment.
Eric Topol, Deep Medicine: How Artificial Intelligence Can Make Healthcare Human Again
Another example is Microsoft which created a radiation AI technology called Project InnerEye. The project demonstrates how AI can improve clinicians’ capacity to arrange radiotherapy 13 times quicker.
Generative AI in Healthcare
Generative AI, currently a trendy topic in the tech world, is entering the health industry. Through the utilisation of artificial intelligence, machine learning and automated processes, generative AI is contributing to facilitating personalised therapy, accelerating drug discovery, enhancing medical imaging analysis, and producing artificial data for research. In addition to improving efficiency and personalisation in healthcare, generative AI is addressing long-standing issues with patient care, diagnosis, and treatment. Hence, generative AI has the potential to completely change the healthcare industry.
2. Integrating Data and Predictive Analysis
Connected with AI and other technologies, data integration and predictive analysis help extract relevant insights about patients’ conditions. Thanks to AI devices, such as robots that enable integrated data and predictive analysis, medical staff have insights into the patient’s medical record, can generate more accurate diagnosis and decide what treatment will work best for them.
Robots collect the data and predict (sometimes before doctors) what will be required for a patient. However, it creates concern about robots’ presence, for example if they can really replace people in their jobs. Such visions are already common in science fiction movies; for example robot ‘Baymax’, known from Big Hero 6, can measure the intensity of a patient’s pain, inform and act when the patient is in danger and point out what medication is required.
Nevertheless, the reality is not exactly the same as movies. AI might not replace doctors but rather help them receive suggested diagnoses, drugs, and treatment plans based on a patient’s specific medical records, history, and present symptoms. Healthcare staff will be able to use the results of big data analytics in healthcare to analyse thousands of patients’ data and improve their outcomes, lower costs, and increase personnel job satisfaction.
3. Nanomedicine
Nanomedicine, or the use of nanotechnology in healthcare, is transforming the medical field by offering highly targeted treatments, increasing the accuracy of diagnostics, and developing novel approaches to challenging medical problems. The technology uses nanobots and nanoparticles, which are hundreds of times smaller than a human hair’s width, for a variety of medical applications, including:
- Targeted drug delivery: Nanoparticles enable direct delivery of drugs to diseased cells, reducing side effects and improving treatment effectiveness.
- Sensing and monitoring: Nanosensors are used for continuous health condition monitoring or early diagnosis since they can detect biological markers at low levels.
- Diagnostics and imaging: Helps with early disease identification by employing nanoparticles to improve the clarity of MRI scans and increase the sensitivity and specificity of diagnostic imaging.
- Regenerative medicine: When it comes to tissue regeneration, nanomaterials imitate or support biological structures. Nano-scaffolds (a medical process used to regenerate bone and tissue, including limbs and organs), on the other hand, encourage cell development for replacement or repair.
- Cancer care: Through targeted chemotherapy administration that spares healthy tissues, enhanced diagnostics for early detection, and the use of nanomaterials to aid in tissue repair following cancer surgery, nanotechnology plays a critical role in the treatment and management of cancer.
- Antimicrobial Treatments: Antimicrobial nanoparticles provide novel approaches to combat bacteria that are resistant to antibiotics, which is crucial for infection management.
Nanomedicine continues to present great opportunities for improving healthcare as research advances, with the potential for more revolutionary responses to long-standing medical issues as well as more effective therapies and enhanced diagnostic tools. It is definitely one of the major trends in healthcare in 2024.
4. Augmented & Virtual Reality in Healthcare
There are several uses for augmented and virtual reality (AR and VR) in healthcare. These technologies allow for connecting the digital and physical environments in a multidimensional way. The development of augmented reality is mainly reliant on artificial intelligence. As already mentioned, cancer can be detected through image recognition. VR can be used in physical therapy in areas like mental trauma, where it can cure phobias. Doctors using AR glasses can overlay CAT scans and 3D scan data to view into the bodies of patients. Some of the designers of glasses that provide mixed reality experiences are Apple with their Apple Vision Pro or Microsoft that designed HoloLens. For instance, the HoloLens glasses were used in surgical planning and have been applied to challenging open-heart procedures, even the entire face transplant performed at Cleveland Clinic.
As technology advances and combines augmented and virtual reality, its utilisation may advance beyond straightforward virtual check-ups to a variety of medical treatments carried out remotely, such as full-fledged surgical operations with the help of automation.
Automation in healthcare is growing and for example, in Japan, there are healthcare robots that care for elderly people. How successful are they? Find out in the video prepared by the Telegraph that highlights Honda’ Hoko Assist’, a replacement for walking sticks or wheelchairs for disabled people that support part of the body.
5.Technology in Mental Health
According to Our World in Data, each year, hundreds of millions experience mental health issues, and many more do so over the course of their lifetimes. One in three women and one in five men are predicted to suffer from serious depression at some point in their life. Therefore, in past years, a number of new technologies in healthcare have been developed that can assist in meeting a patient’s continuing mental health demands. As many things are online now, a lot of psychologists and psychotherapeutics provide their help via video communicators.
There are also Digital Therapeutics (DTx) that serve as software-driven, evidence-based therapeutic interventions for the management, prevention, or treatment of illnesses or diseases. By helping patients manage their symptoms on their own, DTx can enhance various clinical endpoints as well as the patients’ quality of life. To encourage patients to change their behaviour, digital therapeutics employ digital technologies such as smartphones, applications, sensors, virtual reality, the Internet of Things (IoT), and other tools.

Furthermore, AI is incorporated in mental health and is not only common in apps, but it can also be used to identify diseases with symptoms, including a variety of mental symptoms brought on by chemical changes in our brains, for example, dementia. There are many distinct types of dementia, but Alzheimer’s disease is one of the most prevalent types and is characterised by issues with reasoning, memory, and communication. One of the best strategies to treat dementia, or in some circumstances, reverse the origin of symptoms, is early identification.
6. Remote Patient Monitoring & Virtual Care
Internet of Things refers to the overall network of interconnected devices as well as the technology that enables inter-device and inter-cloud communication. The medical industry, often referred to as the IoMT or Telemedicine 2.0 (virtualisation of healthcare services) includes cutting-edge medical technology like wearable sensors, 5G-enabled devices, and remote patient monitoring. For example, Moxa provides smart devices for medical professionals to monitor patients’ vital signs remotely, such as the serial-based bedside monitoring devices that enable medical personnel to monitor their patients’ condition electronically.
One IoT development is a smart pill that gives medical carers and doctors information from inside of the patients’ bodies (called the Internet of Bodies). According to Gartner, smart pills are ingestible sensors that may record various physiological measurements. They can also be used to measure the medication’s effects and verify that a patient has taken it as directed. The first FDA-approved smart pill was released in 2017.
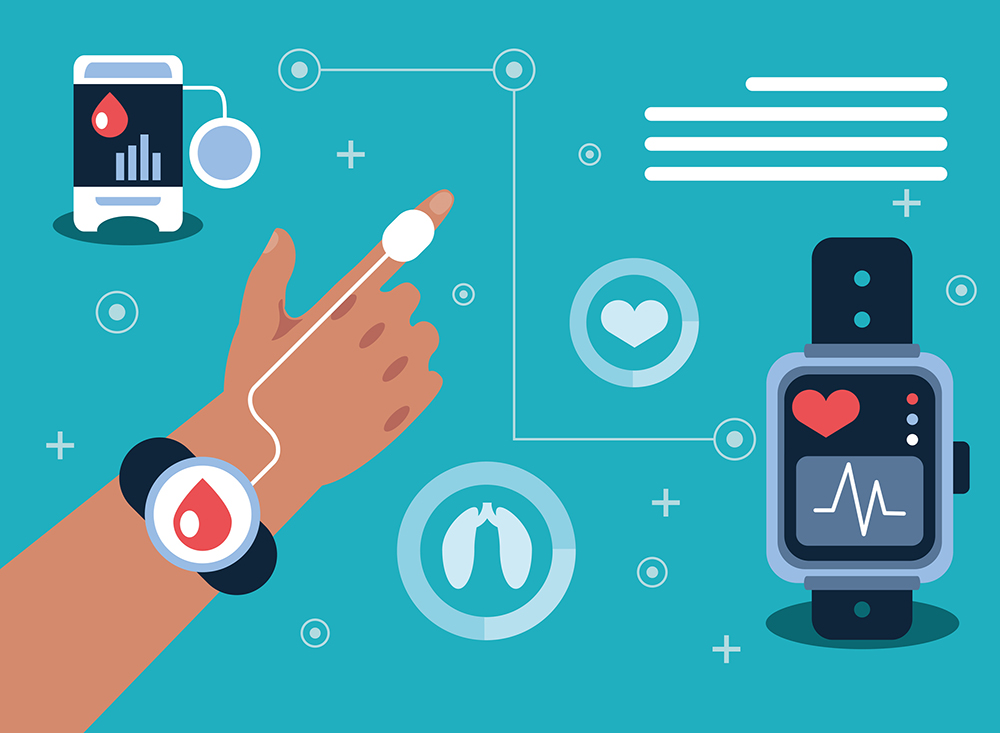

Other features of virtual care include security, location services, telehealth, appointment management, secure messaging, healthcare provider evaluations, and wearable connectivity. Furthermore, primary care facilities and clinics can now serve as virtual hospitals, for example, conducting basic ultrasound examinations on pregnant women and remote data sharing for virtual cooperation.
Chatbots & Virtual Healthcare Assistants
A big transformation in the healthcare industry was led by the introduction of chatbots and virtual healthcare assistants (VHAs). They are transforming preventative healthcare by providing individualised guidance, vaccine and screening reminders, and lifestyle suggestions to lower the risk of chronic illnesses. With real-time engagement, these AI-powered digital assistants give users instant access to health information and encourage them to adopt healthier habits. Through the analysis of user data, they are able to detect any health problems at an early stage and advise people to seek medical attention before things become worse. This is an important part of preventive healthcare and the avoidance of serious health diseases.
The most popular healthcare chatbots are Sensely, Gyant or Youper. See how the last one works in the video below.
7. Digital Twins for Health
Digital twins in healthcare are a revolutionary advancement as the technology can virtually recreate patients’ actual bodies, organs, or health systems to mimic real-world medical situations and forecast results. Unbelievable that with the help of this technology, medical professionals can test procedures, therapies, and interventions on a patient’s virtual twin before implementing them on the actual patient, allowing personalised medicine to reach new heights. It’s especially helpful in complicated circumstances when knowing the possible effects of different treatment alternatives can greatly enhance the decision-making process. Because it is able to predict how diseases will progress or how lifestyle decisions will affect a person’s health, digital twin technology is a potent tool for preventative healthcare. This allows for customised health management plans and early interventions.
8. Wearables in Healthcare
Wearables or wearable technology, mentioned in the Remote Patient Monitoring & Virtual Care section above, is a group of electronic devices that can be worn as an accessory, implanted in the user’s body, incorporated in clothing or even tattooed on the skin. But we will not talk about wearables as gadgets but as important innovations in healthcare. For example, smartwatches allow to remotely check on a patient’s condition by providing information about heart rate, blood oxygen saturation and blood vitals. Wearables such as pedometers and various sensors can also measure a patient’s physical health.
However, smartwatches are not the only wearable improving the medical diagnosis of a patient’s condition, so are biopatch technology and smart hearing aids. Biopatches can give a better insight into a person’s vitals. Hearing aid noise isolation can also be enhanced with artificial intelligence.
9. Organ Care Technology & Bioprinting
3D printing, which we described in the article about Industrial Applications of 3D Printing is a technology behind bioprinting. 3D printing has its application in the healthcare industry through producing such things as external prostheses, cranial or orthopaedic implants, and personalised airway stents.
Ohio State University’s Wexner Medical Center is working on a system that they believe would allow living cells, bones, and eventually even organs to be printed within patients’ bodies by robotic surgery equipment. Something that could save the lives of people that fight cancers. This way, we’ve reached something that refers to bioprinting or 3D printed organs. Although it might sound unreal, the idea has already entered clinical trials. Organs being tested in clinical settings for 3D bioprinting include the ears, corneas, bones, and skin.
10. Healthcare Data Management
Healthcare data management is essential for the safe and effective processing of enormous volumes of data from electronic health records (EHRs), medical imaging, and wearables. In health data management, workflows are optimised, patients have personalised therapies, and data analytics, machine learning, and blockchain are used to improve patient care. Because they can anticipate outcomes and detect risk factors, these systems are essential to preventative healthcare. They facilitate research using anonymised data and guarantee adherence to privacy regulations and patient confidentiality. Therefore, managing data systems is crucial for enhancing results, cutting costs, and preserving data security and privacy.
Healthcare data management has the potential to enhance patient health outcomes, lower costs, and encourage a proactive approach to care. Additionally, in order to handle data and privacy concerns within the healthcare sector, robust health data management solutions are made to protect patient data from breaches and unwanted access by guaranteeing its safe gathering, storing, and analysis.
Future Healthcare Technology Trends
Medical care, research, and patient engagement are all being fundamentally changed by healthcare technology. These developments promise to make healthcare more accurate, accessible, and efficient than it has ever been, from genetic personalisation to global telemedicine networks. Improving patient outcomes, increasing the effectiveness of healthcare delivery, and protecting patient data privacy and security continue to be the medical sector’s top priorities as they start to incorporate new technologies and advancements. With robotics and automation, bioprinting, machine learning and AI, we can expect healthcare that is more adaptable, but cooperation across the healthcare ecosystem will be necessary to embrace these changes.
Sustainable Healthcare
As the world strives toward a more sustainable future, healthcare is also trying to contribute to a better environment, for instance, by providing ecolabelling. Ecolabelling worldwide is a voluntary technique of environmental performance certification and labelling. Within a certain category, an ecolabel highlights goods or services that have been shown to be more environmentally friendly.

Therefore, companies invest in eco-friendly label printer systems for labs, hospitals, clinics, and healthcare. Also, medical professionals’ benefit from such printers and print expert pressure-sensitive labels that can label account/patient information, medication, medical alerts, cage cards, and more.
Another method that the healthcare industry focuses on is decarbonisation. With the European Union’s increasingly ambitious decarbonisation goals there is a necessity to take action across all sectors to track and reduce carbon footprint, especially in the healthcare sector as it contributes to 5% of total emissions.
Concluding, measuring the social impact and implementing green solutions in hospital technology by adding new models of care, improving patients diets and choosing more ecological medical equipment are key to creating a better medical environment. Discover our Top 10 Innovative Technologies in the Sustainable Energy Sector.











