The manufacturing industry is one of the most important sectors of the world economy, and despite labour shortages, continued supply chain issues and constant demand for greater efficiencies, it is likely to remain a key as it produces industrial goods for the global market. From automotive to aerospace and from consumer electronics to machinery and robotics, industrial manufacturing is a key driver of innovation and growth.
Innovations like advanced robots, artificial intelligence (AI), and the Internet of Things (IoT) are causing a significant shift in the industrial manufacturing sector. Along with streamlining production procedures, these advancements are opening up doors for productivity and expansion. This article will discuss the modern developments that are changing the manufacturing landscape.
Technology in Smart Manufacturing
Keeping up with technological advancements has become essential in today’s world of rapid changes. The ability of technology to improve and revolutionise our lives has been continuously shown over the last few decades, from the development of smartphones to robots, spatial computing and augmented reality. This was especially noticeable when production had to be managed remotely or when machinery experienced downgrades. Industry leaders and manufacturers need to make integrating cutting-edge technologies a top priority in order to stay ahead of the ever-changing landscape and its challenges.
“Smart manufacturing is expected to help balance supply and demand, enhance product design, optimise manufacturing efficiency, and significantly reduce waste.”
Mordor Intelligence
Manufacturers can use data trends analysis to find inefficiencies and bottlenecks in their production processes, all made possible by smart manufacturing (SM). Computer-integrated manufacturing, high adaptability and quick design updates, digital information technology, and advanced training for a more flexible technical workforce are a few examples of smart manufacturing systems.
Main Benefits of Technology Adoption by Manufacturers
If you are still unsure about the importance of technology in industrial manufacturing, here are some of the main advantages that your company can benefit from:
- Reduce human errors by investing in automation.
- Improve manufacturing efficiency by mostly increasing output and overcoming labour shortages.
- Invest in smart data that can recognise when it’s time for maintenance, allowing it to be scheduled.
- Improve productivity and help save on maintaining machines as it reduces time spent repairing or replacing equipment.
- Allow tracking of the final product and altering it to meet the needs of your customers.
10 Industrial Manufacturing Trends
To prepare your manufacturing department for challenges, company owners, engineers, and technicians must ensure digital transformation. Especially popular in industrial manufacturing trends are still the IoT, Big Data, and additive manufacturing (3D printing). The last one is still one of the most important trends in industrial maintenance.
But the technology is not stopping. With smart factories and industry 5.0, the future is only becoming more and more digital and connected.
1. Predictive maintenance
Predictive maintenance is critical in assisting industrial companies in meeting rising customer demands and achieving digital transformation. Predictive maintenance (PdM) can be used effectively to anticipate when a machine or piece of equipment will require maintenance, enabling planned maintenance and preventing expensive downtime. By predicting possible failures, it is possible to reduce unplanned downtime, increase the life of machines and save costs.
Manufacturers can use predictive analytics to track equipment performance using a variety of performance parameters and automate the data collection process with IoT technologies. That helps them ensure that all equipment operates at optimal capacity levels.
2. Advanced automation
Automation is one of the key elements of modern industrial manufactures. Many tasks that formerly required human intervention can now be automated thanks to modern software programmes and robotics. The decrease of human involvement in repetitive and hazardous operations makes the manufacturing line safer and more beneficial for factories.

Industrial robots help companies speed up the working process and predict problems and flaws during the manufacturing process. Thanks to robotics, especially the agricultural and manufacturing industries benefit from this technology. According to Markets and Markets, by 2028, the global market for agricultural robots is anticipated to be valued at USD 40.1 billion, expanding at a CAGR of 24.3% over the course of the forecast period.
3. Industry 5.0
The improvement of many manufacturers was dependent on Industry 4.0, sometimes referred to as Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) or smart manufacturing. There’s no questioning the Industry 4.0 impact on manufacturers in improving operational visibility, lowering costs, shortening manufacturing times, and providing superior customer service. It marries digital transformation of manufacturing, production and operations. And the revolution connected with Industry 4.0 hasn’t stopped.
Manufacturers can now even better utilise advanced tools and technological devices. The focus is moved from Industry 4.0 to Industry 5.0. Whereas the fourth industrial revolution focused on employing technology to optimise manufacturing methods, the fifth is all about connecting man and machine, or human-machine collaboration. Industry 5.0 is here and will certainly transform businesses.
4. Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) emerges as one of the most important manufacturing trends for solving the problem of quickly processing large volumes of data and extracting meaningful insights. AI helps industrial operations in many ways, including inventory management, supply chain visibility, warehousing cost reduction, asset tracking, forecasting accuracy, transportation cost reduction, and quality control.
“There is no doubt that manufacturers are making huge commitments to AI. According to estimates, the global AI in manufacturing market was valued at $3.2 billion in 2023 and is poised to grow to $20.8 billion by 2028.”
6 ways to unleash the power of AI in manufacturing, World Economic Forum
Generative AI is the newest innovation of AI and is considered to be the most advanced and efficient AI technology. Generative AI is a machine learning technology that can generate any type of data. A lot of countries are investing in generative AI, and companies like Siemens are using this technology to improve industrial operations (Industrial AI). This technology helps create a whole new world of possibilities for the manufacturing sector, from production optimisation to better maintenance scheduling and asset management.
5. 3D Printing
Additive manufacturing, commonly referred to as 3D printing, is transforming the industrial manufacturing sector by making it possible to create intricate, personalised components with high efficiency and precision. With major benefits like improved customisation, shorter lead times, and material savings, this technology is perfect for producing customised goods without requiring costly moulds or extensive retooling. 3D printing is a trend that is propelling innovation, cutting costs, and enhancing the responsiveness and flexibility of manufacturing processes, putting it in a position to be a major factor in the industry’s future expansion.
Over the years, additive manufacturing has become a popular choice for many industries, enabling innovations like 3D-printed houses, 3D-printed organs, and 3D-printed cars.
6. Industrial IoT
Through the Internet-based connections of devices, systems, and machines, Industrial IoT (IIoT) is revolutionising the manufacturing industry by facilitating real-time data analysis and exchange. By giving manufacturers information about the performance of their equipment and their production processes, this connectivity improves operational efficiency, predictive maintenance, and process optimisation. IIoT is a trend that promotes smarter manufacturing, lowers downtime, and enhances decision-making.
“The market is witnessing a constant rise in the adoption of IoT, owing to the presence of numerous factors such as technological advancements in wireless network technologies, and strong penetration of Wi-Fi connectivity for machine sensors in factories.“
Industrial Internet of Things Market Size & Share Report 2030, Grand View Research
7. B2B shift to B2C
Many manufacturers have switched from a traditional business-to-business (B2B) approach to a business-to-consumer (B2C) model in recent years. B2C increases profits, helps control brand and prices and provide better data. Thanks to B2C manufacturers can create, test, and push things to market quicker.
However, to reach consumers efficiently, companies need to choose an eCommerce platform that supports both B2B and B2C sales platforms. It must provide a visualisation of all the organisation’s B2B and B2C client contacts, as well as order fulfilment and tracking, secure payments, customer support management, and sales and marketing activity tracking.
8. Onshore not offshore
The last couple of years have caused some issues in the global supply chain, making it more difficult for firms to get materials from other nations. Reshoring facilities and expanding their dependency on countries with which European countries have friendly trade agreements are two important supply chain solutions. As the costs of transportation continue to rise, countries should focus more on increasing sales of their lands.
9. New recruitment strategies
Besides technological trends, recruiting a new workforce can also improve your manufacturing. Manufacturing has faced an unprecedented amount of open skilled labour vacancies, in addition to supply chain shortages. Employers have to focus on providing flexibility and referral bonuses for employee retention. As the demand for manufactured goods grows, the need for new skills also increases. Manufacturing companies should take the opportunity to develop new skills and technologies to attract a more diverse workforce, for instance, through next-gen virtual reality (VR) training.
10. Sustainable manufacturing
The manufacturing industry has made climate change a top focus. It is now a commercial responsibility to manage operations in a sustainable and ecologically responsible manner, according to ESG (environmental, social and governance) rules. Many companies in the sector are already creating economically and environmentally sustainable business methods as the cost of energy and sustainable materials rise. Furthermore, regulations tighten, and customers and investors gravitate toward more sustainable brands and business practices.
For instance, agriculture is responsible for around one-third of worldwide greenhouse gas emissions, prompting businesses to reconsider their business models and shift to low-carbon or carbon-neutral manufacturing processes. The green manufacturing tendency will continue as more manufacturers connect sustainability and profit.
Building the Factory of the Future
Despite the difficulties mentioned at the beginning of this article, the industry is expected to grow. The most important is to initiate all the changes and reimagine the future of companies. Manufacturers should fully embrace Industry 5.0 and be open to new technologies. The main trends in industrial manufacturing are moving towards autonomic technology, B2C and carbon neutral. Besides these trends, the manufacturing sector will concentrate on improving cybersecurity and on employee retention and diversity.
Preparing factories and employees for the changes requires innovative thinking, careful planning, and modern systems. Help with it can Asset Operations Management. It’s a comprehensive solution that incorporates enterprise software at the top, as well as predictive analytics and machine learning technologies.
Recommended products
Digital Input Graphical Panel Meters, Red Lion
The latest NPI PM-50 series of panel meters are designed to increase operator productivity and expose critical plant floor data for use in project scheduling and process improvements. It’s the first devices to make the power of Industry 4.0 truly accessible, with smart device connectivity, the meters feature on-board wi-fi, rs-485/modbus, and optional Ethernet or rs-232, with easy start up wizard and app for programming and monitoring.

CP2 Programmable Logic Controllers, Omron
Micro PLC CP2 series of Compact Controllers offers a machine-to-machine communication with data collection thanks to built-in 2-ports Ethernet; control and machine monitoring are not only easy but also improve productivity and support predictive maintenance.

I/O Module 16 DI Ethernet/MODBUS/TCP/EtherNet/IP, Moxa
These Ethernet-connected remote I/O modules with digital and analogue inputs and outputs are simple to connect, control, and monitor. Active contact with SCADA systems is supported using OPC. There are two Ethernet connections for convenient daisy chaining, and there is no need for a switch. With temperature sensors and digital and analogue input monitoring

The Acti9 iEM2000 series energy meters, Schneider
These power monitoring meters offer data measurement with Active energy Class 1 accuracy, LCD display, two tariffs, and MID-approved technology, ideal for sub-billing and cost allocation applications to lower the cost of operation and optimise power efficiency. With the power management software, the Acti9 energy meters transform to a truly IoT digital power installation solution.

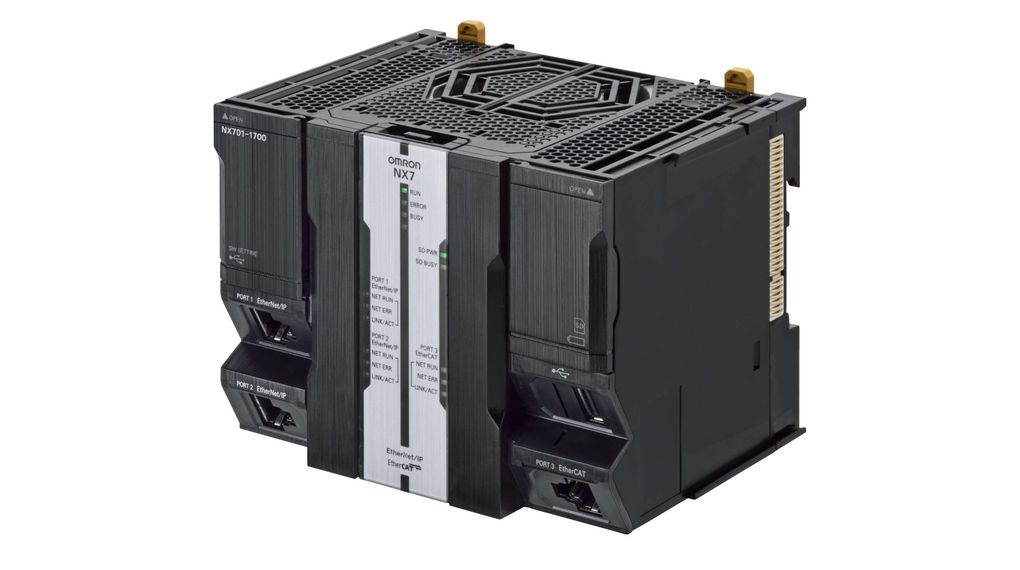
Sysmac NX7 Programmable Logic Controllers, Omron
These AI Machine Automation Controllers allow machine learning and optimisation on edge with fast and accurate control by synchronising all EtherCAT devices, such as vision sensors, servo drives, and field devices, and any anomaly detection to visualise error locations. NX7 AL Controllers encourage people-machine harmonious cooperation to make data-driven decisions, with just-in-time maintenance and replacement, to minimise downtime and reduce production losses.












